SDS capillary gel electrophoresis of proteins in microfabricated channels
- PMID: 10318890
- PMCID: PMC21866
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5372
SDS capillary gel electrophoresis of proteins in microfabricated channels
Abstract
Analysis of variations in the concentrations or structures of biomolecules (e.g., mRNAs, proteins, peptides, natural products) that occur either naturally or in response to environmental or genetic perturbations can provide important insight into complex biological processes. Many biological samples are mixtures that require a separation step before quantitation of variations in the individual components. Two-dimensional denaturing gel electrophoresis has been used very effectively to separate complex mixtures of proteins, but it is time consuming and requires considerable amounts of sample. Microchannel-based separations have proven very effective in rapidly separating small amounts of nucleic acids; more recently, isoelectric focusing of proteins also has been adapted to the microchannel format. Here, we describe microchannel-based SDS capillary gel electrophoresis of proteins and demonstrate the speed and high resolution it provides. This development is an important step toward the miniaturization and integration of multidimensional and array separation methods for complex protein mixtures.
Figures
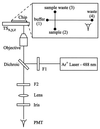

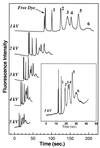

References
-
- James P. Q Rev Biophys. 1997;30:279–331. - PubMed
-
- Celis J E. Drug Discovery Today. 1998;3:193–195.
-
- Celis J E, Gromov P. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1999;10:16–21. - PubMed
-
- Lopez M F. J Chromatogr B. 1999;722:191–202. - PubMed
-
- Haynes P A, Gygi S P, Figeys D, Aebersold R. Electrophoresis. 1998;19:1862–1871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

