Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by the inhibitor K1-5 generated by plasmin-mediated proteolysis
- PMID: 10318952
- PMCID: PMC21928
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5728
Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by the inhibitor K1-5 generated by plasmin-mediated proteolysis
Abstract
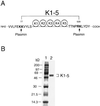
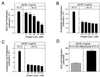
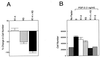
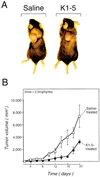
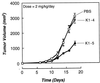
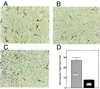
Proteolytic enzymes are involved in generation of a number of endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors. Previously, we reported that angiostatin, a potent angiogenesis inhibitor, is a proteolytic fragment containing the first four kringle modules of plasminogen. In this report, we demonstrate that urokinase-activated plasmin can process plasminogen to release an angiogenesis inhibitor, K1-5 (protease-activated kringles 1-5). K1-5 inhibits endothelial-cell proliferation with a half-maximal concentration of approximately 50 pM. This inhibitory effect is endothelial-cell-specific and appears to be at least approximately 50-fold greater than that of angiostatin. A synergistic efficacy of endothelial inhibition was observed when angiostatin and kringle 5 (K5) were coincubated with capillary endothelial cells. The synergistic effect is comparable to that produced by K1-5 alone. Systemic treatment of mice with K1-5 at a low dose significantly blocked the fibroblast growth factor-induced corneal neovascularization, whereas angiostatin had no effect at the same dose. K1-5 also suppressed angiogenesis in chicken embryos. Systemic administration of K1-5 at a low dose at which angiostatin was ineffective significantly suppressed the growth of a murine T241 fibrosarcoma in mice. The antitumor effect correlates with the reduced neovascularization. These findings suggest that the plasmin-mediated proteolysis may be involved in the negative switch of angiogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Folkman J, Shing Y. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10931–10934. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J, D′Amore P. Cell. 1996;87:1153–1155. - PubMed
-
- Risau W. Nature (London) 1997;386:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J. Cell. 1996;86:353–364. - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly M S, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C, Rosenthal R A, Moses M, Lane W S, Cao Y, Sage E H, Folkman J. Cell. 1994;79:315–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

