Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation mediates 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced parkinsonism
- PMID: 10318960
- PMCID: PMC21936
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5774
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation mediates 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced parkinsonism
Abstract
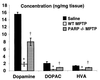
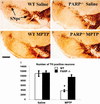
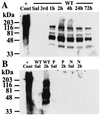
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is a neurotoxin that causes parkinsonism in humans and nonhuman animals, and its use has led to greater understanding of the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. However, its molecular targets have not been defined. We show that mice lacking the gene for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), which catalyzes the attachment of ADP ribose units from NAD to nuclear proteins after DNA damage, are dramatically spared from MPTP neurotoxicity. MPTP potently activates PARP exclusively in vulnerable dopamine containing neurons of the substantia nigra. MPTP elicits a novel pattern of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of nuclear proteins that completely depends on neuronally derived nitric oxide. Thus, NO, DNA damage, and PARP activation play a critical role in MPTP-induced parkinsonism and suggest that inhibitors of PARP may have protective benefit in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Figures
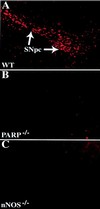
References
-
- Hornykiewicz O. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1992;94:S9–S11. - PubMed
-
- Fahn S. Cecil’s Textbook of Medicine. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1988.
-
- Youdim M B, Riederer P. Sci Am. 1997;276:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Olanow C W. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:439–444. - PubMed
-
- Forno L S, DeLanney L E, Irwin I, Langston J W. Adv Neurol. 1993;60:600–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

