Aquaporin-6: An intracellular vesicle water channel protein in renal epithelia
- PMID: 10318966
- PMCID: PMC21942
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5808
Aquaporin-6: An intracellular vesicle water channel protein in renal epithelia
Abstract
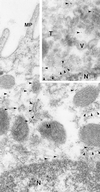
All characterized mammalian aquaporins (AQPs) are localized to plasma membranes where they function chiefly to mediate water transport across cells. Here we show that AQP6 is localized exclusively in intracellular membranes in renal epithelia. By using a polyclonal antibody to the C terminus of AQP6, immunoblots revealed a major 30-kDa band in membranes from rat renal cortex and medulla. Endoglycosidase treatment demonstrated presence of an intracellular high mannose glycan on each subunit. Sequential ultracentrifugation of rat kidney homogenates confirmed that AQP6 resides predominantly in vesicular fractions, and immunohistochemical and immunoelectron microscopic studies confirmed that >98% of AQP6 is located in intracellular membrane vesicles. In glomeruli, AQP6 is present in membrane vesicles within podocyte cell bodies and foot processes. In proximal tubules, AQP6 is also abundant in membrane vesicles within the subapical compartment of segment 2 and segment 3 cells, but was not detected in the brush border or basolateral membranes. In collecting duct, AQP6 resides in intracellular membrane vesicles in apical, mid, and basolateral cytoplasm of type A intercalated cells, but was not observed in the plasma membrane. Unlike other members of the AQP family, the unique distribution in intracellular membrane vesicles in multiple types of renal epithelia indicates that AQP6 is not simply involved in transcellular fluid absorption. Moreover, our studies predict that AQP6 participates in distinct physiological functions such as glomerular filtration, tubular endocytosis, and acid-base metabolism.
Figures




References
-
- Agre P, Bonhivers M, Borgnia M J. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14659–14662. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen S, Marples D, Frøkiær J, Knepper M A, Agre P. Kidney Int. 1996;49:1718–1723. - PubMed
-
- Denker B M, Smith B L, Kuhajda F P, Agre P. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:15634–15642. - PubMed
-
- Sabolic I, Valenti G, Verbavatz J M, Van Hoek A N, Verkman A S, Ausiello D A, Brown D. Am J Physiol. 1992;263:C1225–C1233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

