Assessment of hearing in 80 inbred strains of mice by ABR threshold analyses
- PMID: 10320101
- PMCID: PMC2855304
- DOI: 10.1016/s0378-5955(99)00003-9
Assessment of hearing in 80 inbred strains of mice by ABR threshold analyses
Abstract
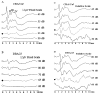
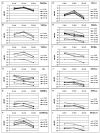
The common occurrence of hearing loss in both humans and mice, and the anatomical and functional similarities of their inner ears, attest to the potential of mice being used as models to study inherited hearing loss. A large-scale, auditory screening project is being undertaken at The Jackson Laboratory (TJL) to identify mice with inherited hearing disorders. To assess hearing sensitivity, at least five mice from each inbred strain had auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds determined. Thus far, we have screened 80 inbred strains of mice; 60 of them exhibited homogeneous ABR threshold values not significantly different from those of the control strain CBA/CaJ. This large database establishes a reliable reference for normal hearing mouse strains. The following 16 inbred strains exhibited significantly elevated ABR thresholds before the age of 3 months: 129/J, 129/ReJ, 129/SvJ, A/J, ALR/LtJ, ALS/LtJ, BUB/BnJ, C57BLKS/J, C57BR/cdJ, C57L/J, DBA/2J, I/LnJ, MA/MyJ, NOD/LtJ, NOR/LtJ, and SKH2/J. These hearing impaired strains may serve as models for some forms of human non-syndromic hearing loss and aid in the identification of the underlying genes.
Figures
References
-
- Atchley WR, Fitch W. Genetic affinities of inbred mouse strains of uncertain origin. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993;10:1150–1169. - PubMed
-
- Brown SD, Steel KP. Genetic deafness – progress with mouse models. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994;3(Spec. No):1453–1546. - PubMed
-
- Church MW, Shucard DW. Age-related hearing loss in BDF1 mice as evidenced by the brainstem auditory evoked potential. Audiology. 1986;25:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Deol MS. A gene for uncomplicated deafness in the mouse. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1956;4:190–195.
-
- Ehret G. Psychoacoustics. In: Willot JF, editor. Auditory Psychobiology of the Mouse. Charles C. Thomas; Springfield, IL: 1983. pp. 13–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

