Differential regulation of glucocorticoid receptor messenger RNA (GR-mRNA) by maternal deprivation in immature rat hypothalamus and limbic regions
- PMID: 10320766
- PMCID: PMC3139462
- DOI: 10.1016/s0165-3806(99)00031-0
Differential regulation of glucocorticoid receptor messenger RNA (GR-mRNA) by maternal deprivation in immature rat hypothalamus and limbic regions
Abstract
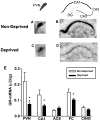
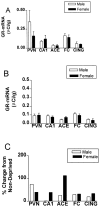
Maternal deprivation (MDep) of neonatal rats significantly influences the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This study hypothesized that GR-mRNA modulation constituted an early, critical mechanism for the acute effects of MDep on neuroendocrine stress-responses. GR-mRNA hybridization signal in hippocampal CA1, hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and frontal cortex was significantly reduced immediately following 24 h MDep. In amygdala, cingulate cortex, PVN and CA1, apparent gender-dependent MDep effects on GR-mRNA expression were observed, without significant differences in absolute levels. Thus, rapid, region-specific MDep effects on GR-mRNA expression in HPA-regulating areas are shown, consistent with involvement of GR-expression in mechanisms of MDep influence on HPA tone.
Copyright 1999 Elsevier Science B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Halasz I, Rittenhouse PA, Zorrilla EP, Redei E. Sexually dimorphic effects of maternal adrenalectomy on hypothalamic CRF, GR and anterior pituitary POMC mRNA levels in rat neonates. Dev Brain Res. 1997;100:198–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

