Functional evidence of alpha1D-adrenoceptors in the vasculature of young and adult spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 10323583
- PMCID: PMC1565938
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702468
Functional evidence of alpha1D-adrenoceptors in the vasculature of young and adult spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
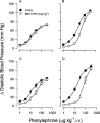
The role of alpha1D-adrenoceptors in the vasculature of spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) and normotensive Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY), of different ages was assessed in pithed rats by the use of the selective alpha1D-adrenoceptor antagonist BMY 7378 (8-[2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]-ethyl]-8-azaspiro [4.5]decane-7,9-dione dihydrochloride). BMY 7378 displaced the pressor effect of phenylephrine in young pre-hypertensive pithed SHR rats, but produced no effect in young WKY rats (dose ratio of 3.4 and 1.6, respectively), while in adult rats BMY 7378 produced a greater shift in the phenylephrine response curve than in younger animals (dose ratio of 3.2 and 6.2 in WKY and SHR, respectively). The presence of alpha1D-adrenoceptors in the vasculature of pre-hypertensive rats, suggests its role in the pathogenesis/maintenance of increased blood pressure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adventitia removal does not modify the alphaID-adrenoceptors response in aorta during hypertension and ageing.Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2009 Jul;29(3):117-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2009.00432.x. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19566752
-
Yohimbine antagonises α1A- and α1D-adrenoceptor mediated components in addition to the α2A-adrenoceptor component to pressor responses in the pithed rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar 15;679(1-3):90-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Jan 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22290390
-
Low concentrations of angiotensin II unmask vasoconstrictory alpha 2-adrenoceptors in isolated perfused kidneys of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Cardiovasc Res. 1995 Dec;30(6):857-65. Cardiovasc Res. 1995. PMID: 8746199
-
Vascular alpha 1D-adrenoceptors have a role in the pressor response to phenylephrine in the pithed rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 1996 Jun 3;305(1-3):173-6. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(96)00229-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8813549
-
Vascular alpha 1D-adrenoceptors: are they related to hypertension?Arch Med Res. 1999 Sep-Oct;30(5):347-52. doi: 10.1016/s0188-0128(99)00047-0. Arch Med Res. 1999. PMID: 10596451 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for involvement of alpha1D-adrenoceptors in contraction of femoral resistance arteries using knockout mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec;146(7):942-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706395. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16170328 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological role of a constitutively active population of alpha(1D)-adrenoceptors in arteries of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;135(1):206-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704447. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11786496 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C-delta1 modulates sustained contraction of rat mesenteric small arteries in response to noradrenaline, but not endothelin-1.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):H826-34. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01396.2007. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18567701 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxyl terminus-truncated α1D-adrenoceptors inhibit the ERK pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;389(8):911-20. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1254-2. Epub 2016 May 5. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27146292 Free PMC article.
-
The alpha(1D)-adrenergic receptor directly regulates arterial blood pressure via vasoconstriction.J Clin Invest. 2002 Mar;109(6):765-75. doi: 10.1172/JCI14001. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 11901185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- HIEBLE J.P., BYLUND D.B., CLARK D.E., EIKENBURG D.C., LANGER S.Z., LEFKOWITZ R.J., MINNEMAN K.P., RUFFOLO R.R., JR International Union of Pharmacology X. Recommendation for nomenclature of α1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995;47:267–270. - PubMed
-
- IBARRA M., LÓPEZ-GUERRERO J.J., VILLALOBOS-MOLINA R. Further evidence for the predominance of α1D-adrenoceptors in arteries of normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacol. Rev. Comm. 1998;10:135–142.
-
- IBARRA M., TERRÓN J.A., LÓPEZ-GUERRERO J.J., VILLALOBOS-MOLINA R. Evidence for an age-dependent functional expression of α1D-adrenoceptors in the rat vasculature. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;322:221–224. - PubMed
-
- PIASCIK M.T., HROMETZ S.L., EDELMANN S.E., GUARINO R.D., HADLEY R.W., BROWN R.D. Immunocytochemical localization of the alpha-1B adrenergic receptor and the contribution of this and other subtypes to vascular smooth muscle contraction: analysis with selective ligands and antisense oligonucleotides. J. Pharmacol. Expt. Ther. 1997;283:854–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

