In vivo effects of new inhibitors of catechol-O-methyl transferase
- PMID: 10323601
- PMCID: PMC1565943
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702474
In vivo effects of new inhibitors of catechol-O-methyl transferase
Abstract
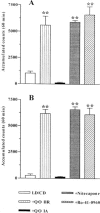
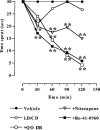
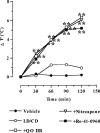
1. The effects of two new synthetic compounds showing in vitro catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitor properties were studied in vivo and compared with the effects of nitecapone and Ro-41-0960. 2. QO IA (3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-5-nitrobenzylidene)-2,4-pentanedione), QO IIR ([2-(3,4-dihydroxy-2-nitrophenyl)vinyl]phenyl ketone), nitecapone and Ro-41-0960 (30 mg kg(-1), i.p.) were given to reserpinized rats 1 h before the administration of L-DOPA/carbidopa (LD/CD, 50:50 mg kg(-1), i.p.). Locomotor activity was assessed 1 h later. All the COMT inhibitors (COMTI), with the exception of QO IA, markedly potentiated LD/CD reversal of reserpine-induced akinesia. Similar results were obtained when the COMTI were coadministered with LD/CD. The effect of compound QO IIR was dose-dependent (7.5-30 mg kg(-1), i.p.). 3. The COMTI (30 mg kg(-1), i.p.) potentiated LD/CD reversal of both catalepsy and hypothermia of reserpinized mice. 4. QO IIR, nitecapone and Ro-41-0960 (30 mg kg(-1), i.p.) reduced striatal 3-methyl-DOPA (3-OMD) levels and increased dopamine (DA) and dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) levels. Compound QO IA was devoid of any effect on striatal amine levels. In contrast to the other inhibitors, Ro-41-0961 reduced HVA levels as well. The effect of QO IIR on striatal amine levels was dose-dependent (7.5-60 mg kg(-1), i.p.) 5. These results suggest that the new compound QO IIR is an effective peripherally acting COMT inhibitor in vivo.
Figures
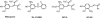
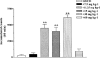
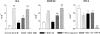
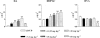
Similar articles
-
Neurochemical and psychomotor interactions of new selective COMT inhibitors with clorgyline and nomifensine in levodopa-treated rats and mice.Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1992 Nov-Dec;320:5-20. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1992. PMID: 1300941
-
Effects of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors and L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine with or without carbidopa on extracellular dopamine in rat striatum.J Neurochem. 1993 Jan;60(1):137-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb05831.x. J Neurochem. 1993. PMID: 8417137
-
Effect of high single doses of levodopa and carbidopa on brain dopamine and its metabolites: modulation by selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and/or catechol-O-methyltransferase in the male rat.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;344(4):412-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00172580. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991. PMID: 1766471
-
Favorable effect of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibition by OR-462 in experimental models of Parkinson's disease.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Oct;247(1):289-93. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988. PMID: 3171977
-
Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors in preclinical models as adjuncts of L-dopa treatment.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010;95:191-205. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381326-8.00008-9. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 21095463 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological activation of mGlu4 metabotropic glutamate receptors reduces nigrostriatal degeneration in mice treated with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 5;26(27):7222-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1595-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16822979 Free PMC article.
-
Sitagliptin and Liraglutide Modulate L-dopa Effect and Attenuate Dyskinetic Movements in Rotenone-Lesioned Rats.Neurotox Res. 2019 Apr;35(3):635-653. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-9998-3. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30673988
-
Beneficial effects of natural phenolics on levodopa methylation and oxidative neurodegeneration.Brain Res. 2013 Feb 25;1497:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.11.043. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23206800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADLER C.H., SINGER C., O'BRIEN C., HAUSER R.A., LEW M.F., MAREK K.L., DORFLINGER E., PEDDER S., DEPTULA D., YOO K. Randomized, placebo-controlled study of tolcapone in patients with fluctuating Parkinson disease treated with levodopa-carbidopa. Tolcapone Fluctuator Study Group III. Arch. Neurol. 1998;55:1089–1095. - PubMed
-
- BÄCKSTRÖM R., HONKANEN E., PIPPURI A., KAIRISALO P., PYSTYNEN J., HEINOLA K., NISSINEN E., LINDÉN I.-B., MÄNNISTO P.T., PHTO P. Synthesis of some novel potent and selective catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 1989;32:841–846. - PubMed
-
- BARTHOLINI G., PLETSCHER A. Decarboxylase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1975;1:407–421. - PubMed
-
- BAAS H., BEISKE A.G., GHIKA J., JACKSON M., OERTEL W.H., POEWE W., RANSMAYR G. Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibition with tolcapone reduces the ‘wearing off' phenomenon and levodopa requirements in fluctuating parkinsonian patients. Neurology. 1998;50 Suppl. 5:S46–S53. - PubMed
-
- BORGULYA J., BRUDERER H., BERNAUER K., ZÜRCHER G., DA PRADA G. Catechol-O-methyltransferase-inhibiting pyrocatechol derivatives: synthesis and structure-activity studies. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1989;72:952–968.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

