CDC group IV c-2: a new Ralstonia species close to Ralstonia eutropha
- PMID: 10325323
- PMCID: PMC84948
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.6.1777-1781.1999
CDC group IV c-2: a new Ralstonia species close to Ralstonia eutropha
Abstract
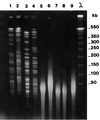
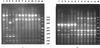
CDC group IV c-2, an environmental gram-negative bacillus recently proposed for inclusion in the genus Ralstonia, has been isolated in several human infections. Biochemical characterization and 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequencing with phylogenetic analysis were used to characterize eight clinical isolates and four type strains. Other typing tools, such as pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis, were also used. PFGE typing of clinical isolates was unsuccessful because the DNA was degraded, and RAPD analysis was poorly discriminatory. In contrast, the type strains were clearly distinguished with both PFGE and RAPD analysis. All of the 16S rDNA sequences were identical. Comparison of the 16S rDNA sequences to the GenBank sequences showed that they were consistent with CDC group IV c-2 belonging to the genus Ralstonia. The closest matches were obtained with Ralstonia eutropha. However, four differences in 32 biochemical tests separated R. eutropha from CDC group IV c-2, which suggests that CDC group IV c-2 is a new species of the genus Ralstonia.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Altwegg M, Zollinger-Iten J. Identification of Enterobacteriaceae, Aeromonas spp. and Plesiomonas shigelloides with the ATB 32-GN system. J Microbiol Methods. 1987;7:103–109.
-
- Arance A, Montes A, Cismal M, Mesia R, Falo C, Garcia del Muro J, Germa J R. CDC group IV c-2 infection in a stem cell transplant recipient. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997;11:1005–1006. - PubMed
-
- Aspinall S T, Graham R. Two sources of contamination of a hydrotherapy pool by environmental organisms. J Hosp Infect. 1989;14:285–292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

