Design and evaluation of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA assay using nucleic acid sequence-based amplification technology able to quantify both group M and O viruses by using the long terminal repeat as target
- PMID: 10325329
- PMCID: PMC84958
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.6.1813-1818.1999
Design and evaluation of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA assay using nucleic acid sequence-based amplification technology able to quantify both group M and O viruses by using the long terminal repeat as target
Abstract
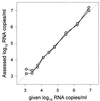
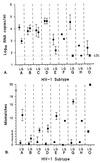
Currently available human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA quantification assays can detect most viruses of the group M subtypes, but a substantial number are missed or not quantified reliably. Viruses of HIV-1 group O cannot be detected by any commercially available assay. We developed and evaluated a quantitative assay based on nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) technology, with primers and probes located in the conserved long terminal repeat (LTR) region of the HIV-1 genome. In 68 of 72 serum samples from individuals infected with HIV-1 subtypes A to H of group M, viruses could be detected and quantified. In serum samples from two patients infected with HIV-1 group O viruses, these viruses as well could be detected and quantified. In contrast, the currently used gag-based assay underestimated the presence of subtype A viruses and could not detect subtype G and group O viruses. The discrepancy between the results of the two assays may be explained by the number of mismatches found within and among the probe and primer regions of the subtype isolates. These data indicate that LTR-based assays, including the NASBA format chosen here, are better suited to monitoring HIV-1 therapy than are gag-based assays in an era in which multiple HIV-1 subtypes and groups are spreading worldwide.
Figures


References
-
- Alaeus A, Lidman K, Sonnerborg A, Albert J. Subtype-specific problems with quantification of plasma HIV-1 RNA. AIDS. 1997;11:859–865. - PubMed
-
- Arnold C, Barlow K L, Kaye S, Loveday C, Balfe P, Clewley J P. HIV type 1 sequence subtype G transmission from mother to infant: failure of variant sequence species to amplify in the Roche Amplicor Test. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1995;11:999–1001. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn G F, Shah H P, Kenten J H, Leland J, Kamin R A, Link J, Peterman J, Powell M J, Shah A, Talley D B, Tyagi S K, Wilkins E, Wu T-G, Massey R J. Electrochemiluminescence detection for development of immunoassays and DNA probe assays for clinical diagnostics. Clin Chem. 1991;37:1534–1539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

