Localization of the platelet-activating factor receptor to rat pancreatic microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 10329588
- PMCID: PMC1866601
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65389-8
Localization of the platelet-activating factor receptor to rat pancreatic microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
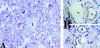
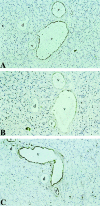
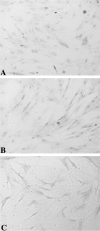
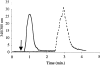
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a potent lipid autocoid involved in numerous inflammatory processes. Although PAF plays a key role as a mediator of inflammation in acute pancreatitis, the site(s) of action of PAF in the pancreas remains unknown. One of the aims of this study was to identify cell types within the pancreas expressing the PAF receptor using immunohistochemical protocols. Additionally, pancreatic microvascular endothelial cells were isolated and examined for the PAF receptor using immunohistochemistry, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, and intracellular calcium responses to PAF exposure. Immunohistochemical analysis of pancreatic slices using an antibody directed toward the N-terminus of the PAF receptor revealed specific localization to the vascular endothelium with no localization to other pancreatic cell types. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction of RNA isolated from cultured pancreatic islet endothelial cells yielded the predicted amplicon for the PAF receptor. Cultured pancreatic islet endothelial cells responded to PAF as measured by a transient increase in intracellular calcium, which was ameliorated in the presence of a PAF receptor antagonist. The results demonstrate the localization of PAF receptors on the pancreatic vascular endothelium. The presence of PAF receptors on the pancreatic vascular endothelium provides a defined, highly localized target for therapeutic intervention.
Figures

References
-
- Hanahan DJ, Demopoulos CA, Liehr J, Pinckard RN: Identification of platelet activating factor isolated from rabbit basophils as acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem 1980, 255:5514-5516 - PubMed
-
- Camussi G, Montrucchio G, Lupia E, De Martino A, Perona L, Arese M, Vercellone A, Toniolo A, Bussolino F: Platelet-activating factor directly stimulates in vitro migration of endothelial cells and promotes in vivo angiogenesis by a heparin-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 1995, 154:6492-6501 - PubMed
-
- Frenkel RA, Muguruma K, Johnston JM: The biochemical role of platelet-activating factor in reproduction. Prog Lipid Res 1996, 35:155-168 - PubMed
-
- Ayala A, Chaudry IH: Platelet activating factor and its role in trauma, shock, and sepsis. New Horiz 1996, 4:265-275 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

