VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer
- PMID: 10329591
- PMCID: PMC1866582
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65392-8
VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer
Abstract
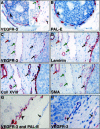
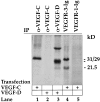
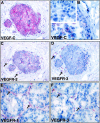
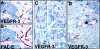
Recently, monoclonal antibodies against the human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor VEGFR-3 were shown to provide a specific antigenic marker for lymphatic endothelium in various normal tissues. In this study we have investigated the expression of VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C in normal breast tissue and in breast tumors by immunohistochemistry. VEGFR-3 was weakly expressed in capillaries of normal breast tissue and in fibroadenomas. In intraductal breast carcinomas, VEGFR-3 was prominent in the "necklace" vessels adjacent to the basal lamina of the tumor-filled ducts. VEGF receptor 1 and 2 as well as blood vessel endothelial and basal lamina markers were colocalized with VEGFR-3 in many of these vessels. Antibodies against smooth muscle alpha-actin gave a weak staining of the necklace vessels, suggesting that they were incompletely covered by pericytes/smooth muscle cells. A highly elevated number of VEGFR-3 positive vessels was found in invasive breast cancer in comparison with histologically normal breast tissue (P < 0.0001, the Mann-Whitney test). VEGF-C was located in the cytoplasm of intraductal and invasive cancer cells. The results demonstrate that the expression of VEGFR-3 becomes up-regulated in the endothelium of angiogenic blood vessels in breast cancer. The results also suggest that VEGF-C secreted by the intraductal carcinoma cells acts predominantly as an angiogenic growth factor for blood vessels, although this paracrine signaling network between the cancer cells and the endothelium may also be involved in modifying the permeabilities of both blood and lymphatic vessels and metastasis formation.
Figures

References
-
- Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T: The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev 1997, 18:4-25 - PubMed
-
- Shibuya M: Role of VEGF-FLT receptor system in normal and tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res 1995, 67:281-316 - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N: The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the regulation of angiogenesis. Kidney Int 1999, In press - PubMed
-
- Clauss M, Weich H, Breier G, Knies U, Rockl W, Waltenberger J, Risau W: The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flt-1 mediates biological activities: Implications for a functional role of placenta growth factor in monocyte activation and chemotaxis. J Biol Chem 1996, 271:17629-17634 - PubMed
-
- Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, Ferrara N: Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362:841-844 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

