Distinct CXC chemokines mediate tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 10329603
- PMCID: PMC1866583
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65404-1
Distinct CXC chemokines mediate tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells
Abstract
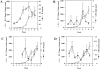
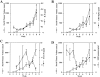
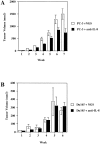
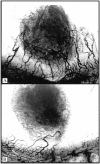
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of malignancy-related mortality in males in the United States. As a solid tumor, clinically significant tumor growth and metastasis are dependent on nutrients and oxygen supplied by tumor-associated neovasculature. As such, there is a selective tumorigenic advantage for those neoplasms that can produce angiogenic mediators. We show here that human prostate cancer cell lines can constitutively produce angiogenic CXC chemokines. Tumorigenesis of PC-3 prostate cancer cells was shown to be attributable, in part, to the production of the angiogenic CXC chemokine, interleukin (IL)-8. Neutralizing antisera to IL-8 inhibits PC-3 tumor growth in a human prostate cancer/SCID mouse model. Furthermore, angiogenic activity in PC-3 tumor homogenates was attributable to IL-8. In contrast, the Du145 prostate cancer cell line uses a different angiogenic CXC chemokine, GRO-alpha, to mediate tumorigenicity. Neutralizing antisera to GRO-alpha but not IL-8 reduced tumor growth in vivo and reduced the angiogenic activity in tumor homogenates. Thus, prostate cancer cell lines can use distinct CXC chemokines to mediate their tumorigenicity.
Figures


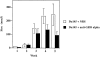
References
-
- Parker S, Tong T, Bolden S, Wingo P: Cancer statistics, 1996. Cancer J Clin 1996, 46:5-27 - PubMed
-
- Maiorana A, Gullino PM: Acquisition of angiogenic capacity and neoplastic transformation in the rat mammary gland. Cancer Res 1978, 38:4409-4414 - PubMed
-
- Bouck N: Tumor angiogenesis: the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cancer Cells 1990, 2:179-185 - PubMed
-
- Walz A, Kunkel SL, Strieter RM: CXC chemokines-an overview: chemokines in disease. Edited by AE Koch, RM Strieter. Austin, TX, R.G. Landes, 1996, pp 1–26
-
- Strieter RM, Kunkel SL: Chemokines and the lung. Lung: Scientific Foundations, 2nd edition. R Crystal, J West, E Weibel, P Weibel. New York, Raven Press, 1997, pp 155–186
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

