Genomic structure and comparative analysis of nine Fugu genes: conservation of synteny with human chromosome Xp22.2-p22.1
- PMID: 10330123
- PMCID: PMC310778
Genomic structure and comparative analysis of nine Fugu genes: conservation of synteny with human chromosome Xp22.2-p22.1
Abstract
The pufferfish Fugu rubripes has a compact 400-Mb genome that is approximately 7.5 times smaller than the human genome but contains a similar number of genes. Focusing on the distal short arm of the human X chromosome, we have studied the evolutionary conservation of gene orders in Fugu and man. Sequencing of 68 kb of Fugu genomic DNA identified nine genes in the following order: (SCML2)-STK9, XLRS1, PPEF-1, KELCH2, KELCH1, PHKA2, AP19, and U2AF1-RS2. Apart from an evolutionary inversion separating AP19 and U2AF1-RS2 from PHKA2, gene orders are identical in Fugu and man, and all nine human homologs map to the Xp22 band. All Fugu genes were found to be smaller than their human counterparts, but gene structures were mostly identical. These data suggest that genomic sequencing in Fugu is a powerful and economical strategy to predict gene orders in the human genome and to elucidate the structure of human genes.
Figures



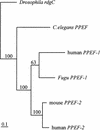


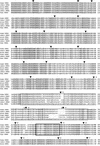

References
-
- Aparicio S, Brenner S. How good a model is the Fugu genome. Nature. 1997;387:140. - PubMed
-
- Armes N, Gilley J, Fried M. The comparative genomic structure and sequence of the surfeit gene homologs in the puffer fish Fugu rubripes and their association with CpG-rich islands. Genome Res. 1997;7:138–152. - PubMed
-
- Baxendale S, Abdulla S, Elgar G, Buck D, Berks M, Micklem G, Durbin R, Bates G, Brenner S, Beck S. Comparative sequence analysis of the human and pufferfish Huntington’s disease genes. Nat Genet. 1995;10:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Bork P, Doolittle RF. Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J Mol Biol. 1994;236:1277–1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
