Fluorescence polarization in homogeneous nucleic acid analysis
- PMID: 10330129
- PMCID: PMC310763
Fluorescence polarization in homogeneous nucleic acid analysis
Abstract
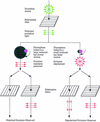
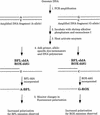
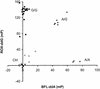
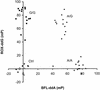
A new method for DNA diagnostics based on template-directed primer extension and detection by fluorescence polarization is described. In this method, amplified genomic DNA containing a polymorphic locus is incubated with oligonucleotide primers (designed to hybridize to the DNA template adjacent to the polymorphic site) in the presence of allele-specific dye-labeled dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates and a commercially available modified Taq DNA polymerase. The primer is extended by the dye-terminator specific for the allele present on the template, increasing approximately 10-fold the molecular weight of the fluorophore. At the end of the reaction, the fluorescence polarization of the two dye-terminators in the reaction mixture are analyzed directly without separation or purification. This homogeneous DNA diagnostic method is shown to be highly sensitive and specific and is suitable for automated genotyping of large number of samples. [The data shown in Figure 3 are available as an online supplement at.]
Figures
References
-
- Alford RL, Caskey CT. DNA analysis in forensics, disease and animal/plant identification. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1994;5:29–33. - PubMed
-
- Checovich WJ, Bolger RE, Burke T. Fluorescence polarization—A new tool for cell and molecular biology [published erratum appears in Nature 1995; 375:520] Nature. 1995;375:254–256. - PubMed
-
- Cooper DN, Clayton JF. DNA polymorphism and the study of disease associations. Hum Genet. 1988;78:299–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
