Efficient approach to unique single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery
- PMID: 10330130
- PMCID: PMC310784
Efficient approach to unique single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery
Abstract
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most frequently found DNA sequence variations in the human genome. It has been argued that a dense set of SNP markers can be used to identify genetic factors associated with complex disease traits. Because all high-throughput genotyping methods require precise sequence knowledge of the SNPs, any SNP discovery approach must involve both the determination of DNA sequence and allele frequencies. Furthermore, high-throughput genotyping also requires a genomic DNA amplification step, making it necessary to develop sequence-tagged sites (STSs) that amplify only the DNA fragment containing the SNP and nothing else from the rest of the genome. In this report, we demonstrate the utility of a SNP-screening approach that yields the DNA sequence and allele frequency information while screening out duplications with minimal cost and effort. Our approach is based on the use of a homozygous complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) as the reference. With this homozygous reference, one can identify and estimate the allele frequencies of common SNPs with a pooled DNA-sequencing approach (rather than having to sequence numerous individuals as is commonly done). More importantly, the CHM reference is preferable to a single individual reference because it reveals readily any duplicated regions of the genome amplified by the PCR assay before the duplicated sequences are found in GenBank. This approach reduces the cost of SNP discovery by 60% and eliminates the costly development of SNP markers that cannot be amplified uniquely from the genome.
Figures

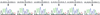
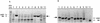
References
-
- Collins FS, Guyer MS, Chakravarti A. Variations on a theme: Cataloging human DNA sequence variation. Science. 1997;278:1580–1581. - PubMed
-
- Dausset J, Cann H, Cohen D, Lathrop M, Lalouel JM, White R. Centre d’etude du polymorphisme humain (CEPH): Collaborative genetic mapping of the human genome. Genomics. 1990;6:575–577. - PubMed
-
- Eichler EE, Lu F, Shen Y, Antonacci R, Jurecic V, Doggett NA, Moyzis RK, Baldini A, Gibbs RA, Nelson DL. Duplication of a gene-rich cluster between 16p11.1 and Xq28: A novel pericentromeric-directed mechanism for paralogous genome evolution. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:899–912. - PubMed
-
- Eichler EE, Budarf ML, Rocchi M, Deaven LL, Doggett NA, Baldini A, Nelson DL, Mohrenweiser HW. Interchromosomal duplications of the adrenoleukodystrophy locus: A phenomenon of pericentromeric plasticity. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:991–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
