Protein kinase B/Akt participates in GLUT4 translocation by insulin in L6 myoblasts
- PMID: 10330141
- PMCID: PMC104360
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.4008
Protein kinase B/Akt participates in GLUT4 translocation by insulin in L6 myoblasts
Abstract
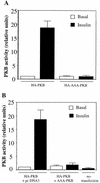
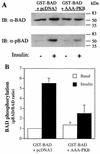
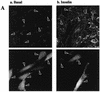
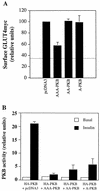
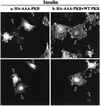
L6 myoblasts stably transfected with a GLUT4 cDNA harboring an exofacial myc epitope tag (L6-GLUT4myc myoblasts) were used to study the role of protein kinase B alpha (PKBalpha)/Akt1 in the insulin-induced translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface. Surface GLUT4myc was detected by immunofluorescent labeling of the myc epitope in nonpermeabilized cells. Insulin induced a marked translocation of GLUT4myc to the plasma membrane within 20 min. This was prevented by transient transfection of a dominant inhibitory construct of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase (Deltap85alpha). Transiently transfected cells were identified by cotransfection of green fluorescent protein. A constitutively active PKBalpha, created by fusion of a viral Gag protein at its N terminus (GagPKB), increased the cell surface density of GLUT4myc compared to that of neighboring nontransfected cells. A kinase-inactive, phosphorylation-deficient PKBalpha/Akt1 construct with the mutations K179A (substitution of alanine for the lysine at position 179), T308A, and S473A (AAA-PKB) behaved as a dominant-negative inhibitor of insulin-dependent activation of cotransfected wild-type hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged PKB. Furthermore, AAA-PKB markedly inhibited the insulin-induced phosphorylation of cotransfected BAD, demonstrating inhibition of the endogenous PKB/Akt. Under the same conditions, AAA-PKB almost entirely blocked the insulin-dependent increase in surface GLUT4myc. PKBalpha with alanine substitutions T308A and S473A (AA-PKB) or K179A (A-PKB) alone was a less potent inhibitor of insulin-dependent activation of wild-type HA-PKB or GLUT4myc translocation than was AAA-PKB. Cotransfection of AAA-PKB with a fourfold DNA excess of HA-PKB rescued insulin-stimulated GLUT4myc translocation. AAA-PKB did not prevent actin bundling (membrane ruffling), though this response was PI 3-kinase dependent. Therefore, it is unlikely that AAA-PKB acted by inhibiting PI 3-kinase signaling. These results outline an important role for PKBalpha/Akt1 in the stimulation of glucose transport by insulin in muscle cells in culture.
Figures




References
-
- Alessi D R, Deak M, Casamayor A, Caudwell F B, Morrice N, Norman D G, Gaffney P, Reese C B, MacDougall C N, Harbison D, Ashworth A, Bownes M. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr Biol. 1997;7:776–789. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, James S R, Downes C P, Holmes A B, Gaffney P R, Reese C B, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase B alpha. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay G, Standaert M L, Galloway L, Moscat J, Farese R V. Evidence for involvement of protein kinase C (PKC)-zeta and noninvolvement of diacylglycerol-sensitive PKCs in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in L6 myotubes. Endocrinology. 1997;138:4721–4731. - PubMed
-
- Brown R E, Jarvis K L, Hyland K J. Protein measurement using bicinchoninic acid: elimination of interfering substances. Anal Biochem. 1989;180:136–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
