Protein kinase Cdelta mediates neurogenic but not mitogenic activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in neuronal cells
- PMID: 10330161
- PMCID: PMC104380
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.4209
Protein kinase Cdelta mediates neurogenic but not mitogenic activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in neuronal cells
Abstract
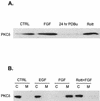
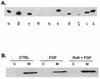
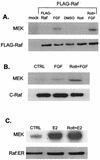
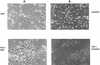
In several neuronal cell systems, fibroblast-derived growth factor (FGF) and nerve growth factor (NGF) act as neurogenic agents, whereas epidermal growth factor (EGF) acts as a mitogen. The mechanisms responsible for these different cellular fates are unclear. We report here that although FGF, NGF, and EGF all activate mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (extracellular signal-related kinase [ERK]) in rat hippocampal (H19-7) and pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells, the activation of ERK by the neurogenic agents FGF and NGF is dependent upon protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta), whereas ERK activation in response to the mitogenic EGF is independent of PKCdelta. Antisense PKCdelta oligonucleotides or the PKCdelta-specific inhibitor rottlerin inhibited FGF- and NGF-induced, but not EGF-induced, ERK activation. In contrast, EGF-induced ERK activation was inhibited by the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor wortmannin, which had no effect upon FGF-induced ERK activation. Rottlerin also inhibited the activation of MAP kinase kinase (MEK) in response to activated Raf, but had no effect upon c-Raf activity or ERK activation by activated MEK. These results indicate that PKCdelta functions either downstream from or in parallel with c-Raf, but upstream of MEK. Inhibition of PKCdelta also blocked neurite outgrowth induced by FGF and NGF in PC12 cells and by activated Raf in H19-7 cells, indicating a role for PKCdelta in the neurogenic effects of FGF, NGF, and Raf. Interestingly, the PKCdelta requirement is apparently cell type specific, since FGF-induced ERK activation was independent of PKCdelta in NIH 3T3 murine fibroblasts, in which FGF is a mitogen. These data demonstrate that PKCdelta contributes to growth factor specificity and response in neuronal cells and may also promote cell-type-specific differences in growth factor signaling.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Different protein kinase C isoforms determine growth factor specificity in neuronal cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;20(15):5392-403. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.15.5392-5403.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10891480 Free PMC article.
-
Divergence in the anti-apoptotic signalling pathways used by nerve growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in PC12 cells: rescue by bFGF involves protein kinase C delta.Biochem J. 2000 Nov 15;352 Pt 1(Pt 1):175-82. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 11062070 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase for neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells.J Biol Chem. 1998 Sep 18;273(38):24285-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.38.24285. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9733710
-
Nck inhibits NGF and basic FGF induced PC12 cell differentiation via mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent pathway.Oncogene. 1996 Jun 6;12(11):2351-9. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8649775
-
Role of MAP kinase in neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 1998 Feb;16(1):79-95. doi: 10.1007/BF02740604. Mol Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9554703 Review.
Cited by
-
Borna disease virus blocks potentiation of presynaptic activity through inhibition of protein kinase C signaling.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Mar;2(3):e19. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020019. Epub 2006 Mar 17. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 16552443 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular actions of neurotrophins.Physiol Rev. 2009 Jan;89(1):279-308. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00007.2008. Physiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19126759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and genetic basis of depression.J Genet. 2014 Dec;93(3):879-92. doi: 10.1007/s12041-014-0449-x. J Genet. 2014. PMID: 25572252 Review.
-
Microtubule-dependent subcellular redistribution of the transcriptional coactivator p/CIP.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;22(18):6611-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.18.6611-6626.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12192059 Free PMC article.
-
Mediation of basic fibroblast growth factor-induced lactotropic cell proliferation by Src-Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase p44/42 signaling.Endocrinology. 2005 Apr;146(4):1948-55. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1448. Epub 2005 Jan 6. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15637287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chao T-S O, Byron K L, Lee K-M, Villereal M, Rosner M R. Activation of MAP kinase by calcium-dependent and calcium-independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:19876–19883. - PubMed
-
- Chou M M, Hou W, Johnson J, Graham L K, Lee M H, Chen C-S, Newton A C, Schaffhausen B S, Toker A. Regulation of protein kinase Cζ by PI 3-kinase and PDK-1. Curr Biol. 1998;8:1069–1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
