Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in activation of ras and mitogen-activated protein kinase by epidermal growth factor
- PMID: 10330169
- PMCID: PMC104388
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.4279
Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in activation of ras and mitogen-activated protein kinase by epidermal growth factor
Abstract
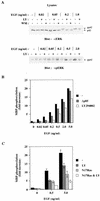
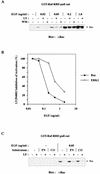
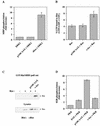
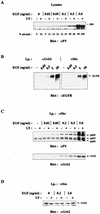
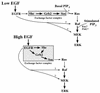
The paradigm for activation of Ras and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase by extracellular stimuli via tyrosine kinases, Shc, Grb2, and Sos does not encompass an obvious role for phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase, and yet inhibitors of this lipid kinase family have been shown to block the ERK/MAP kinase signalling pathway under certain circumstances. Here we show that in COS cells activation of both endogenous ERK2 and Ras by low, but not high, concentrations of epidermal growth factor (EGF) is suppressed by PI 3-kinase inhibitors; since Ras activation is less susceptible than ERK2 activation, PI 3-kinase-sensitive events may occur both upstream of Ras and between Ras and ERK2. However, strong elevation of PI 3-kinase lipid product levels by expression of membrane-targeted p110alpha is by itself never sufficient to activate Ras or ERK2. PI 3-kinase inhibition does not affect EGF-induced receptor autophosphorylation or adapter protein phosphorylation or complex formation. The concentrations of EGF for which PI 3-kinase inhibitors block Ras activation induce formation of Shc-Grb2 complexes but not detectable EGF receptor phosphorylation and do not activate PI 3-kinase. The activation of Ras by low, but mitogenic, concentrations of EGF is therefore dependent on basal, rather than stimulated, PI 3-kinase activity; the inhibitory effects of LY294002 and wortmannin are due to their ability to reduce the activity of PI 3-kinase to below the level in a quiescent cell and reflect a permissive rather than an upstream regulatory role for PI 3-kinase in Ras activation in this system.
Figures


References
-
- Bos J L. Ras-like GTPases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333:M19–M31. - PubMed
-
- Bos J L, Franke B, M’Rabet L, Reedquist K, Zwartkruis F. In search of a function for the Ras-like GTPase Rap1. FEBS Lett. 1997;410:59–62. - PubMed
-
- Buday L, Downward J. EGF regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993;73:611–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
