Ajuba, a novel LIM protein, interacts with Grb2, augments mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in fibroblasts, and promotes meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes in a Grb2- and Ras-dependent manner
- PMID: 10330178
- PMCID: PMC104397
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.4379
Ajuba, a novel LIM protein, interacts with Grb2, augments mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in fibroblasts, and promotes meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes in a Grb2- and Ras-dependent manner
Abstract
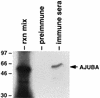
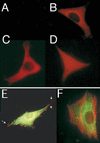
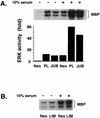
LIM domain-containing proteins contribute to cell fate determination, the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation, and remodeling of the cell cytoskeleton. These proteins can be found in the cell nucleus, cytoplasm, or both. Whether and how cytoplasmic LIM proteins contribute to the cellular response to extracellular stimuli is an area of active investigation. We have identified and characterized a new LIM protein, Ajuba. Although predominantly a cytosolic protein, in contrast to other like proteins, it did not localize to sites of cellular adhesion to extracellular matrix or interact with the actin cytoskeleton. Removal of the pre-LIM domain of Ajuba, including a putative nuclear export signal, led to an accumulation of the LIM domains in the cell nucleus. The pre-LIM domain contains two putative proline-rich SH3 recognition motifs. Ajuba specifically associated with Grb2 in vitro and in vivo. The interaction between these proteins was mediated by either SH3 domain of Grb2 and the N-terminal proline-rich pre-LIM domain of Ajuba. In fibroblasts expressing Ajuba mitogen-activated protein kinase activity persisted despite serum starvation and upon serum stimulation generated levels fivefold higher than that seen in control cells. Finally, when Ajuba was expressed in fully developed Xenopus oocytes, it promoted meiotic maturation in a Grb2- and Ras-dependent manner.
Figures

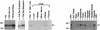



Similar articles
-
Meltrin alpha cytoplasmic domain interacts with SH3 domains of Src and Grb2 and is phosphorylated by v-Src.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 30;19(51):5842-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203986. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11127814
-
Signal transduction pathways triggered by fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes after fibroblast growth factor 1 addition. Role of Grb2, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Src tyrosine kinase, and phospholipase Cgamma.Eur J Biochem. 2000 Oct;267(20):6256-63. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01710.x. Eur J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11012680
-
Interactive roles of Ras, insulin receptor substrate-1, and proteins with Src homology-2 domains in insulin signaling in Xenopus oocytes.J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27645-9. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7961682
-
Inhibitors of Ras signal transduction as antitumor agents.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1165-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00428-7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007954 Review.
-
AJUBA: A regulator of epidermal homeostasis and cancer.Exp Dermatol. 2021 Apr;30(4):546-559. doi: 10.1111/exd.14272. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Exp Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33372298 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of zyxin in signal transduction and its relationship with diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 22;11:1371549. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1371549. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38712343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The LIM protein Ajuba promotes adipogenesis by enhancing PPARγ and p300/CBP interaction.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jan;23(1):158-68. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.83. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26113042 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Aurora-A kinase on the mitotic spindle.Chromosoma. 2003 Dec;112(4):159-63. doi: 10.1007/s00412-003-0265-1. Epub 2003 Nov 21. Chromosoma. 2003. PMID: 14634755 Review.
-
JUB induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Mar 1;11(3):1374-1382. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938233 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved LIM domain-containing focal adhesion protein ZYX-1 regulates synapse maintenance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Development. 2014 Oct;141(20):3922-33. doi: 10.1242/dev.108217. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Development. 2014. PMID: 25252943 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
