Disrupted differentiation and oncogenic transformation of lymphoid progenitors in E2A-HLF transgenic mice
- PMID: 10330184
- PMCID: PMC104403
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.4443
Disrupted differentiation and oncogenic transformation of lymphoid progenitors in E2A-HLF transgenic mice
Abstract
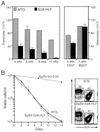
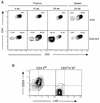
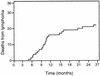
The hepatic leukemia factor (HLF) gene codes for a basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP) protein that is disrupted by chromosomal translocations in a subset of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemias. HLF undergoes fusions with the E2A gene, resulting in chimeric E2a-Hlf proteins containing the E2a transactivation domains and the Hlf bZIP DNA binding and dimerization motifs. To investigate the in vivo role of this chimeric bZIP protein in oncogenic transformation, its expression was directed to the lymphoid compartments of transgenic mice. Within the thymus, E2a-Hlf induced profound hypoplasia, premature involution, and progressive accumulation of a T-lineage precursor population arrested at an early stage of maturation. In the spleen, mature T cells were present but in reduced numbers, and they lacked expression of the transgene, suggesting further that E2a-Hlf expression was incompatible with T-cell differentiation. In contrast, mature splenic B cells expressed E2a-Hlf but at lower levels and without apparent adverse or beneficial effects on their survival. Approximately 60% of E2A-HLF mice developed lymphoid malignancies with a mean latency of 10 months. Tumors were monoclonal, consistent with a requirement for secondary genetic events, and displayed phenotypes of either mid-thymocytes or, rarely, B-cell progenitors. We conclude that E2a-Hlf disrupts the differentiation of T-lymphoid progenitors in vivo, leading to profound postnatal thymic depletion and rendering B- and T-cell progenitors susceptible to malignant transformation.
Figures


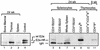

References
-
- Ardavin C, Wu L, Li C L, Shortman K. Thymic dendritic cells and T cells develop simultaneously in the thymus from a common precursor population. Nature. 1993;362:761–763. - PubMed
-
- Bain G, Murre C. The role of E-proteins in B- and T-lymphocyte development. Semin Immunol. 1998;10:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Bindl J M, Warnke R A. Advantages of detecting monoclonal antibody binding to tissue sections with biotin and avidin reagents in coplin jars. Am J Pathol. 1986;85:490–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
