p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1) regulates cell motility in mammalian fibroblasts
- PMID: 10330410
- PMCID: PMC2133181
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.4.837
p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1) regulates cell motility in mammalian fibroblasts
Abstract
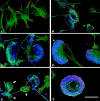
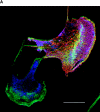
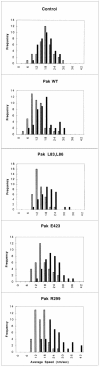
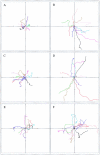
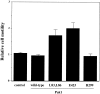
The p21 (Cdc42/Rac) activated kinase Pak1 regulates cell morphology and polarity in most, if not all, eukaryotic cells. We and others have established that Pak's effects on these parameters are mediated by changes in the organization of cortical actin. Because cell motility requires polarized rearrangements of the actin/myosin cytoskeleton, we examined the role of Pak1 in regulating cell movement. We established clonal tetracycline-regulated NIH-3T3 cell lines that inducibly express either wild-type Pak1, a kinase-dead, or constitutively-active forms of this enzyme, and examined the morphology, F-actin organization, and motility of these cells. Expression of any of these forms of Pak1 induced dramatic changes in actin organization which were not inhibited by coexpression of a dominant-negative form of Rac1. Cells inducibly expressing wild-type or constitutively-active Pak1 had large, polarized lamellipodia at the leading edge, were more motile than their normal counterparts when plated on a fibronectin-coated surface, and displayed enhanced directional movement in response to an immobilized collagen gradient. In contrast, cells expressing a kinase-dead form of Pak1 projected multiple lamellipodia emerging from different parts of the cell simultaneously. These cells, though highly motile, displayed reduced persistence of movement when plated on a fibronectin-coated surface and had defects in directed motility toward immobilized collagen. Expression of constitutively activated Pak1 was accompanied by increased myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation, whereas expression of kinase-dead Pak1 had no effect on MLC. These results suggest that Pak1 affects the phosphorylation state of MLC, thus linking this kinase to a molecule that directly affects cell movement.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human p21-activated kinase (Pak1) regulates actin organization in mammalian cells.Curr Biol. 1997 Mar 1;7(3):202-10. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(97)70091-5. Curr Biol. 1997. PMID: 9395435
-
Temporal and spatial distribution of activated Pak1 in fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1449-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1449. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134074 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of macropinocytosis by p21-activated kinase-1.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Oct;11(10):3341-52. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.10.3341. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 11029040 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal regulation of the Pak1 kinase.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):646-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0330646. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042564 Review.
-
The p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1) signalling pathway in cardiac disease: from mechanistic study to therapeutic exploration.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;175(8):1362-1374. doi: 10.1111/bph.13872. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28574147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential role of p21 Activated Kinase 1 (PAK1) in the invasion and motility of oral cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2016 May 16;16 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2263-8. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27229476 Free PMC article.
-
Central nervous system functions of PAK protein family: from spine morphogenesis to mental retardation.Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Aug;34(1):67-80. doi: 10.1385/mn:34:1:67. Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17003522 Review.
-
A Pak- and Pix-dependent branch of the SDF-1alpha signalling pathway mediates T cell chemotaxis across restrictive barriers.Biochem J. 2006 Jul 1;397(1):213-22. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051655. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16515536 Free PMC article.
-
A Rac-cGMP signaling pathway.Cell. 2007 Jan 26;128(2):341-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.048. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17254971 Free PMC article.
-
Pak1 and Pak2 mediate tumor cell invasion through distinct signaling mechanisms.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;28(12):4162-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01532-07. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18411304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen WE, Jones GE, Pollard JW, Ridley AJ. Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 regulate actin organization and cell adhesion in macrophages. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:707–720. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Anand-Apte B, Zetter B, Viswanathan A, Qiu R-g, Chen J, Ruggieri R, Symons M. PDGF and fibronectin-stimulated migration are differentially regulated by the Rac and ERK pathways. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30688–30692. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S, Taylor SJ, Jordon KA, Van Aelst L, Cerione RA. A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23633–23636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

