Paxillin LD4 motif binds PAK and PIX through a novel 95-kD ankyrin repeat, ARF-GAP protein: A role in cytoskeletal remodeling
- PMID: 10330411
- PMCID: PMC2133183
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.4.851
Paxillin LD4 motif binds PAK and PIX through a novel 95-kD ankyrin repeat, ARF-GAP protein: A role in cytoskeletal remodeling
Abstract
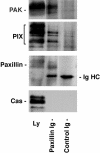
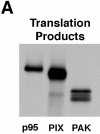
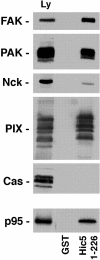
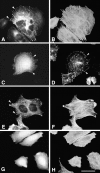
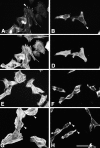
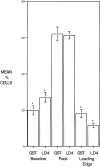
Paxillin is a focal adhesion adaptor protein involved in the integration of growth factor- and adhesion-mediated signal transduction pathways. Repeats of a leucine-rich sequence named paxillin LD motifs (Brown M.C., M.S. Curtis, and C.E. Turner. 1998. Nature Struct. Biol. 5:677-678) have been implicated in paxillin binding to focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and vinculin. Here we demonstrate that the individual paxillin LD motifs function as discrete and selective protein binding interfaces. A novel scaffolding function is described for paxillin LD4 in the binding of a complex of proteins containing active p21 GTPase-activated kinase (PAK), Nck, and the guanine nucleotide exchange factor, PIX. The association of this complex with paxillin is mediated by a new 95-kD protein, p95PKL (paxillin-kinase linker), which binds directly to paxillin LD4 and PIX. This protein complex also binds to Hic-5, suggesting a conservation of LD function across the paxillin superfamily. Cloning of p95PKL revealed a multidomain protein containing an NH2-terminal ARF-GAP domain, three ankyrin-like repeats, a potential calcium-binding EF hand, calmodulin-binding IQ motifs, a myosin homology domain, and two paxillin-binding subdomains (PBS). Green fluorescent protein- (GFP-) tagged p95PKL localized to focal adhesions/complexes in CHO.K1 cells. Overexpression in neuroblastoma cells of a paxillin LD4 deletion mutant inhibited lamellipodia formation in response to insulin-like growth fac- tor-1. Microinjection of GST-LD4 into NIH3T3 cells significantly decreased cell migration into a wound. These data implicate paxillin as a mediator of p21 GTPase-regulated actin cytoskeletal reorganization through the recruitment to nascent focal adhesion structures of an active PAK/PIX complex potentially via interactions with p95PKL.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Paxillin-dependent paxillin kinase linker and p21-activated kinase localization to focal adhesions involves a multistep activation pathway.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 May;13(5):1550-65. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-02-0015. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12006652 Free PMC article.
-
Actopaxin, a new focal adhesion protein that binds paxillin LD motifs and actin and regulates cell adhesion.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1435-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1435. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134073 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of LIM3 as the principal determinant of paxillin focal adhesion localization and characterization of a novel motif on paxillin directing vinculin and focal adhesion kinase binding.J Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;135(4):1109-23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.4.1109. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8922390 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin interactions.J Cell Sci. 2000 Dec;113 Pt 23:4139-40. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.23.4139. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 11069756 Review.
-
Paxillin: a focal adhesion-associated adaptor protein.Oncogene. 2001 Oct 1;20(44):6459-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204786. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11607845 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of ARF6 by ARNO stimulates epithelial cell migration through downstream activation of both Rac1 and phospholipase D.J Cell Biol. 2001 Aug 6;154(3):599-610. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200104019. Epub 2001 Jul 30. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11481345 Free PMC article.
-
The integrin-actin connection, an eternal love affair.EMBO J. 2003 May 15;22(10):2324-33. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg245. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12743027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimal features of paxillin that are required for the tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase.Biochem J. 2006 Jan 15;393(Pt 2):565-73. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051241. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16253116 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef selectively associates with a catalytically active subpopulation of p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) independently of PAK2 binding to Nck or beta-PIX.J Virol. 2001 Mar;75(5):2154-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.5.2154-2160.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160719 Free PMC article.
-
The GIT-PIX complexes regulate the chemotactic response of rat basophilic leukaemia cells.Biol Cell. 2010 Jan 14;102(4):231-44. doi: 10.1042/BC20090074. Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 19912111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam L, Vadlamuda R, Kondapaka B, Chernoff J, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R. Heregulin regulates cytoskeletal reorganization and cell migration through the p21-activated kinase-1 via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28238–28246. - PubMed
-
- Ayi TC, Tsan JT, Hwang LY, Bowcock AM, Baer R. Conservation of function and primary structure in the BRCA1-associated RING domain (BARD1) protein. Oncogene. 1998;17:2143–2148. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S, Taylor SJ, Creasy CL, Chernoff J, Cerione RA. Identification of a mouse p21Cdc42/Racactivated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:22731–22737. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S, Taylor SJ, Jordan KA, Van Aelst L, Cerione RA. A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23633–23636. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., D. Bailey, Z. Leonard, M. Hart, J.-L. Guan, R.T. Premont, S.J. Taylor, and R.A. Cerione. 1999. A tyrosine phosphorylated protein that binds to an important regulatory region on the Cool family of Pak-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. In press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

