Cytochrome P450 isoforms involved in metabolism of the enantiomers of verapamil and norverapamil
- PMID: 10336579
- PMCID: PMC2014179
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00923.x
Cytochrome P450 isoforms involved in metabolism of the enantiomers of verapamil and norverapamil
Abstract
Aims: The present study was conducted to evaluate metabolism of the enantiomers of verapamil and norverapamil using a broad range of cytochrome P450 isoforms and measure the kinetic parameters of these processes.
Methods: Cytochrome P450 cDNA-expressed cells and microsomes from a P450-expressed lymphoblastoid cell line were incubated with 40 microm concentrations of R- or S-verapamil and R- or S-norverapamil and metabolite formation measured by h.p.l.c. as an initial screening. Those isoforms exhibiting substantial activity were then studied over a range of substrate concentrations (2.5-450 microm ) to estimate the kinetic parameters for metabolite formation.
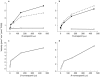
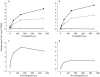
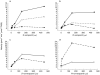
Results: P450s 3A4, 3A5, 2C8 and to a minor extent 2E1 were involved in the metabolism of the enantiomers of verapamil. Estimated Km values for the production of D-617 and norverapamil by P450 s 3A4 and 3A5 were similar (range=60-127 microm ) regardless of the enantiomer of verapamil studied while the Vmax estimates were also similar (range=4-8 pmol min-1 pmol-1 P450). Only nominal production of D-620 by these isoforms was noted. Interestingly, P450 2C8 readily metabolized both S- and R-verapamil to D-617, norverapamil and PR-22 with only slightly higher Km values than noted for P450s 3A4 and 3A5. However, the Vmax estimates for P450 2C8 metabolism of S- and R-verapamil were in general greater (range=8-15 pmol min-1 pmol-1 P450) than those noted for P450 s 3A4 and 3A5 with preference noted for metabolism of the S-enantiomer. Similarly, P450 s 3A4, 3A5 and 2C8 also mediated the metabolism of the enantiomers of norverapamil with minor contributions by P450 s 2D6 and 2E1. P450s 3A4 and 3A5 readily formed the D-620 metabolite with generally a lower Km and higher Vmax for S-norverapamil than for the R-enantiomer. In contrast, P450 2C8 produced both the D-620 and PR-22 metabolites from the enantiomers of norverapamil, again with stereoselective preference seen for the S-enantiomer.
Conclusions: These results confirm that P450s 3A4, 3A5 and 2C8 play a major role in verapamil metabolism and demonstrate that norverapamil can also be further metabolized by the P450s.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Halofantrine metabolism in microsomes in man: major role of CYP 3A4 and CYP 3A5.J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999 Apr;51(4):419-26. doi: 10.1211/0022357991772628. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10385214
-
Identification of three cytochrome P450 isozymes involved in N-demethylation of citalopram enantiomers in human liver microsomes.Pharmacogenetics. 1997 Feb;7(1):1-10. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199702000-00001. Pharmacogenetics. 1997. PMID: 9110356
-
Role of human cytochrome P450 3A4 and 3A5 in the metabolism of taxotere and its derivatives: enzyme specificity, interindividual distribution and metabolic contribution in human liver.Pharmacogenetics. 1998 Oct;8(5):391-401. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199810000-00004. Pharmacogenetics. 1998. PMID: 9825831
-
Cytochromes P450 and metabolism of xenobiotics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 May;58(5-6):737-47. doi: 10.1007/pl00000897. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11437235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereoselectivity of human cytochrome p450 in metabolic and inhibitory activities.Curr Drug Metab. 2011 Jul;12(6):549-69. doi: 10.2174/138920011795713724. Curr Drug Metab. 2011. PMID: 21476971 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic N-Dealkylation and N-Oxidation as Elucidators of the Role of Alkylamino Moieties in Drugs Acting at Various Receptors.Molecules. 2021 Mar 29;26(7):1917. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071917. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33805491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How important are gender differences in pharmacokinetics?Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(5):329-42. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241050-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12036391 Review.
-
Impact of stereoselectivity on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antiarrhythmic drugs.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(8):533-58. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241080-00001. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12102640 Review.
-
Chemical inhibitors of cytochrome P450 isoforms in human liver microsomes: a re-evaluation of P450 isoform selectivity.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2011 Mar;36(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s13318-011-0024-2. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2011. PMID: 21336516 Review.
-
PharmGKB summary: very important pharmacogene information for cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 8.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2013 Dec;23(12):721-8. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283653b27. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23962911 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eichelbaum M, Ende M, Remberg G, Schomerus M, Dengler H. The metabolism of DL-[14C]-verapamil in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1979;7:145–148. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer HK, Gautier JC, Beaune P, Henderson C, Wolf CR, Eichelbaum M. Identification of P450 enzymes involved in metabolism of verapamil in humans. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993;348:332–337. - PubMed
-
- Busse D, Cosme J, Beaune P, Kroemer HK, Eichelbaum M. Cytochromes of the P450, 2C subfamily are the major enzymes involved in the O–demethylation of verapamil in humans. Naunyn–Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995;353:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez FJ, Aoyama T, Gelboin HV. Expression of mammalian cytochrome P450 using vaccinia virus. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:85–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

