Induction in transgenic mice of HLA-A2.1-restricted cytotoxic T cells specific for a peptide sequence from a mutated p21ras protein
- PMID: 10337009
- PMCID: PMC1905280
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00873.x
Induction in transgenic mice of HLA-A2.1-restricted cytotoxic T cells specific for a peptide sequence from a mutated p21ras protein
Abstract
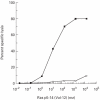
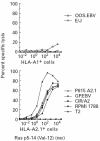
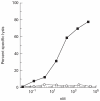
Cytotoxic T cells (CTL) recognize short peptides that are derived from the proteolysis of endogenous cellular proteins and presented on the cell surface as a complex with MHC class I molecules. CTL can recognize single amino acid substitutions in proteins, including those involved in malignant transformation. The mutated sequence of an oncogene may be presented on the cell surface as a peptide, and thus represents a potential target antigen for tumour therapy. The p21ras gene is mutated in a wide variety of tumours and since the transforming mutations result in amino acid substitutions at positions 12, 13 and 61 of the protein, a limited number of ras peptides could potentially be used in the treatment of a wide variety of malignancies. A common substitution is Val for Gly at position 12 of p21ras. In this study, we show that the peptide sequence from position 5 to position 14 with Val at position 12-ras p5-14 (Val-12)-has a motif which allows it to bind to HLA-A2.1. HLA-A2.1-restricted ras p5-14 (Val-12)-specific CTL were induced in mice transgenic for both HLA-A2.1 and human beta2-microglobulin after in vivo priming with the peptide. The murine CTL could recognize the ras p5-14 (Val-12) peptide when they were presented on both murine and human target cells bearing HLA-A2.1. No cross-reactivity was observed with the native peptide ras p5-14 (Gly-12), and this peptide was not immunogenic in HLA-A2.1 transgenic mice. This represents an interesting model for the study of an HLA-restricted CD8 cytotoxic T cell response to a defined tumour antigen in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of a human CD8+ T lymphocyte neo-epitope created by a ras codon 12 mutation which is restricted by the HLA-A2 allele.Cell Immunol. 1998 Aug 1;187(2):103-16. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1998.1325. Cell Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9732698
-
Induction and characterization of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes recognizing a mutated p21ras peptide presented by HLA-A*0201.Int J Cancer. 1995 May 4;61(3):389-96. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910610319. Int J Cancer. 1995. PMID: 7729952
-
Generation of stable CD4+ and CD8+ T cell lines from patients immunized with ras oncogene-derived peptides reflecting codon 12 mutations.Cell Immunol. 1997 Dec 15;182(2):137-51. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1997.1224. Cell Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9514698 Clinical Trial.
-
A single amino acid substitution in HLA-A2 can alter the selection of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte repertoire that responds to influenza virus matrix peptide 55-73.J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):558-64. J Immunol. 1989. PMID: 2472444
-
T-cell immunity to oncogenic proteins including mutated ras and chimeric bcr-abl.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 12;690:101-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb44000.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993. PMID: 8103658 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimized Anchor-Modified Peptides Targeting Mutated RAS Are Promising Candidates for Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:902709. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902709. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Towsend AR, Gotch FM, Davey J. Cytotoxic T cells recognize fragments of the influenza nucleoprotein. Cell. 1985;42:457–67. - PubMed
-
- Maryanski JL, Verdini AS, Weber PC, et al. Competitor analogs for defined T cell antigens: peptides incorporating a putative binding motif and polyproline or polyglycine spacers. Cell. 1990;60:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Lurquin C, Van Pel A, Mariamé B, et al. Structure of the gene of tum- transplantation antigen P91A: the mutated exon encodes a peptide recognized with Ld by cytolytic T cells. Cell. 1989;58:293–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

