Suppression of platelet aggregation by Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin
- PMID: 10338478
- PMCID: PMC96579
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.2763-2768.1999
Suppression of platelet aggregation by Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin
Abstract
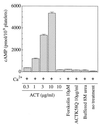
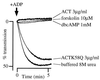
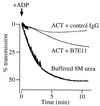
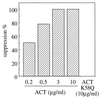
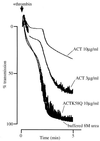
The effect of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin (ACT) on platelet aggregation was investigated. This cell-invasive adenylate cyclase completely suppressed ADP (10 microM)-induced aggregation of rabbit platelets at 3 micrograms/ml and strongly suppressed thrombin (0. 2 U/ml)-induced aggregation at 10 micrograms/ml. The suppression was accompanied by marked increase in platelet intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) content and was diminished by the anti-ACT monoclonal antibody B7E11. A catalytically inactive point mutant of ACT did not show the suppressive effect. Since an increase of cAMP content is a known cause of platelet dysfunction, these results indicate that the observed platelet inactivation was due to the catalytic activity of ACT through increase of intracellular cAMP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase: effects of affinity-purified adenylate cyclase on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions.Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):135-40. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.135-140.1987. Infect Immun. 1987. PMID: 2878884 Free PMC article.
-
Pertussis toxin inhibits cAMP-induced desensitization of adenylate cyclase in Dictyostelium discoideum.Mol Cell Biochem. 1990 Feb 9;92(2):177-89. doi: 10.1007/BF00218135. Mol Cell Biochem. 1990. PMID: 2155382
-
Invasive adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis.Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):459-63. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90106-0. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989. PMID: 2560273 Review.
-
Effects of adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis on human neutrophil interactions with Coccidioides immitis and Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):751-5. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.751-755.1988. Infect Immun. 1988. PMID: 2894360 Free PMC article.
-
Bordatella pertussis adenylate cyclase: a toxin with multiple talents.Trends Microbiol. 1999 Apr;7(4):172-6. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(99)01468-7. Trends Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10217833 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B initiates protein kinase C translocation and eicosanoid metabolism while inhibiting thrombin-induced aggregation in human platelets.Mol Cell Biochem. 2006 Aug;288(1-2):171-8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-006-9134-6. Epub 2006 Mar 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16550298
-
Pathogen analysis of pertussis-like syndrome in children.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 May 19;20(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05074-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32429853 Free PMC article.
-
Initial characterization of the hemolysin stachylysin from Stachybotrys chartarum.Infect Immun. 2001 Feb;69(2):912-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.2.912-916.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11159985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benz R, Maier E, Ladant D, Ullmann A, Šebo P. Adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis: evidence for the formation of small ion-permeable channels and comparison with HlyA of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:27231–27239. - PubMed
-
- Born G V R. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962;194:927–929. - PubMed
-
- Brownlie R M, Coote J G, Parton R, Schultz J E, Rogel A, Hanski E. Cloning of the adenylate cyclase genetic determinant of Bordetella pertussis and its expression in Escherichia coli and B. pertussis. Microb Pathog. 1988;4:335–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

