CD4(+) T cells and the proinflammatory cytokines gamma interferon and interleukin-6 contribute to alveolar bone loss in mice
- PMID: 10338484
- PMCID: PMC96585
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.2804-2809.1999
CD4(+) T cells and the proinflammatory cytokines gamma interferon and interleukin-6 contribute to alveolar bone loss in mice
Abstract
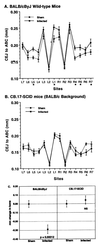
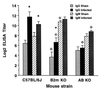
In this study, we used a mouse model to examine the role of the adaptive immune response in alveolar bone loss induced by oral infection with the human gram-negative anaerobic bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis. Severe combined immunodeficient mice, which lack B and T lymphocytes, exhibited considerably less bone loss than did immunocompetent mice after oral infection, suggesting that lymphocytes contribute to this process. Bone loss after oral infection was decreased in mice deficient in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-responsive CD4(+) T cells, but no change in bone loss was observed in mice deficient in MHC class I-responsive CD8(+) T cells or NK1(+) T cells. Mice lacking the cytokine gamma interferon or interleukin-6 also demonstrated decreased bone loss. These results suggest that the adaptive immune response, and in particular CD4(+) T cells and the proinflammatory cytokines that they secrete, are important effectors of bone loss consequent to P. gingivalis oral infection. The studies also reinforce the utility of the mouse oral infection model in dissecting the pathobiology of periodontal disease.
Figures



References
-
- Baker P J, Evans R T, Roopenian D C. Oral infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and induced alveolar bone loss in immunocompetent and severe combined immunodeficient mice. Arch Oral Biol. 1994;39:1035–1040. - PubMed
-
- Baker, P. J., S. Carter, M. Dixon, R. T. Evans, and D. C. Roopenian. Serum antibody response to oral infection precedes but does not prevent Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone loss in mice. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., in press. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Vignery A, Horowitz M. Lymphocytes, macrophages, and the regulation of bone remodeling. In: Peck W A, editor. Bone and mineral research annual 2: a yearly survey of developments in the field of bone and mineral metabolism. New York, N.Y: Elsevier Science Publishers; 1983. pp. 175–243.
-
- Been V, Engel D. The effects of immunosuppressive drugs on periodontal inflammation in human renal allograft patients. J Periodontol. 1982;53:245–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials


