Genes influencing resistance to Coccidioides immitis and the interleukin-10 response map to chromosomes 4 and 6 in mice
- PMID: 10338499
- PMCID: PMC96600
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.2916-2919.1999
Genes influencing resistance to Coccidioides immitis and the interleukin-10 response map to chromosomes 4 and 6 in mice
Abstract
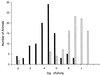
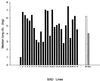
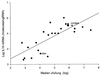
Coccidioidomycosis is a fungal infection that is endemic in the southwestern United States. Infection is more severe in blacks and Filipinos, which suggests that there is a genetic basis for susceptibility to this infection in humans. We found that there is also a difference in resistance to Coccidioides immitis infection among inbred mouse strains: B6 mice are susceptible, while DBA/2 mice are resistant (T. N. Kirkland and J. Fierer, Infect. Immun. 40:912-916, 1983). In this paper we report the results of our efforts to map the genes responsible for resistance to this infection in mice. Mice were infected by intraperitoneal inoculation, and 15 days later the numbers of viable fungi in their lungs and spleens were enumerated. We also determined the amounts of interleukin-10 mRNA made in the infected lungs. These three phenotypes were mapped as quantitative traits by using the 26 available lines of recombinant inbred mice derived from a cross between B6 and DBA/2 mice. The best associations were those between the regions near the Lv locus on chromosome 4 and the Tnfr1 locus on chromosome 6. We then infected backcross mice [(B6 x DBA/2) x B6] and confirmed these associations; 14 of 16 (87%) mice that were heterozygous at both Lv and Tnfr1 were resistant to infection, whereas only 4 of 16 (25%) mice that were homozygous B6 at both loci were resistant. These are the first genetic loci to be associated with susceptibility to C. immitis, but there may be additional genes involved in murine resistance to this infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dectin-1 is required for resistance to coccidioidomycosis in mice.mBio. 2013 Feb 5;4(1):e00597-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00597-12. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23386437 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of interleukin-10 in genetic susceptibility of mice to Coccidioides immitis.Infect Immun. 1998 Sep;66(9):4397-402. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4397-4402.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9712793 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic evidence for the role of the Lv locus in early susceptibility but not IL-10 synthesis in experimental coccidioidomycosis in C57BL mice.J Infect Dis. 2000 Feb;181(2):681-5. doi: 10.1086/315256. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10669355
-
Coccidioides immitis and posadasii; A review of their biology, genomics, pathogenesis, and host immunity.Virulence. 2018;9(1):1426-1435. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1509667. Virulence. 2018. PMID: 30179067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of innate and adaptive immunity to coccidioidomycosis.Med Mycol. 2019 Feb 1;57(Supplement_1):S85-S92. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myy146. Med Mycol. 2019. PMID: 30690602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Susceptibility to Coccidioides species in C57BL/6 mice is associated with expression of a truncated splice variant of Dectin-1 (Clec7a).Genes Immun. 2008 Jun;9(4):338-48. doi: 10.1038/gene.2008.23. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Genes Immun. 2008. PMID: 18418396 Free PMC article.
-
Dectin-1 is required for resistance to coccidioidomycosis in mice.mBio. 2013 Feb 5;4(1):e00597-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00597-12. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23386437 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine Protection of Mice With Primary Immunodeficiencies Against Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 7;11:790488. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.790488. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35071044 Free PMC article.
-
Early Events in Coccidioidomycosis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019 Oct 16;33(1):e00112-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00112-19. Print 2019 Dec 18. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31619396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and Other Determinants for the Severity of Coccidioidomycosis: A Clinician's Perspective.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 May 11;9(5):554. doi: 10.3390/jof9050554. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37233265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ampel N M, Dols C L, Galgiani J N. Coccidioidomycosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection: results of a prospective study in a coccidioidal endemic area. Am J Med. 1993;94:235–240. - PubMed
-
- Cox R A, Vivas J R, Gross A, Lecara G, Miller E, Brummer E. In vivo and in vitro cell-mediated responses in coccidioidomycosis. I. Immunologic responses of persons with primary, asymptomatic infections. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976;114:937–943. - PubMed
-
- Drutz D J, Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;117:559–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

