Levels of gamma interferon and interleukin-4 are inversely related to the levels of their corresponding autoantibodies in patients with lower respiratory tract infection
- PMID: 10338519
- PMCID: PMC96620
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.3051-3054.1999
Levels of gamma interferon and interleukin-4 are inversely related to the levels of their corresponding autoantibodies in patients with lower respiratory tract infection
Abstract
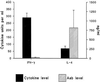
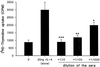
To study the involvement of cytokines and their corresponding autoantibodies (Aabs) in inflammatory mechanisms in patients with lower respiratory tract infections, blood samples were taken from patients at the time of admission to the hospital and before treatment. Cell-released capturing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to measure the levels of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-4 (IL-4) produced spontaneously by peripheral mononuclear cells (PMNC). ELISA was used to measure Aabs to these cytokines in sera. The levels of both cytokines were inversely related to the levels of their corresponding Aabs. While a high level of IFN-gamma was observed together with a low level of anti-IFN-gamma Aab, decreased IL-4 levels were observed with increased levels of Aabs to IL-4. Immunoglobulins were purified, digested to obtain Fab fragments, and tested for specificity and cross-reactivity. The Aabs and their Fab fragments were tested in cytokine biological assays and showed neutralizing effects. Our data demonstrated increased levels of the proinflammatory cytokine IFN-gamma and decreased release of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 during early presentation of lower respiratory tract infection. The levels of these cytokines were inversely related to the levels of their corresponding Aabs that exhibited regulatory effects on the cytokine biological function in vitro.
Figures
References
-
- Arend W P. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:167–227. - PubMed
-
- Bendtzen K, Hansen M B, Ross C, Poulsen L K, Svenson M. Cytokines and autoantibodies to cytokines. Stem Cells. 1995;13:206–222. - PubMed
-
- Bendtzen K, Svenson M, Jonsson V, Hippe E. Autoantibodies to cytokines: friends or foes. Immunol Today. 1990;11:167–169. - PubMed
-
- Chretien I, Pene J, Briere F, de Waal Malefijt R, Rousset F, De Vries J E. Regulation of human IgE synthesis. 1. Human IgE synthesis in vitro is determined by the reciprocal antagonistic effects of interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1990;20:243–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

