Transcriptional activation of mRNA of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and induction of its cell surface expression in normal human gingival fibroblasts by Mycoplasma salivarium and Mycoplasma fermentans
- PMID: 10338521
- PMCID: PMC96622
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.3061-3065.1999
Transcriptional activation of mRNA of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and induction of its cell surface expression in normal human gingival fibroblasts by Mycoplasma salivarium and Mycoplasma fermentans
Abstract
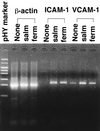
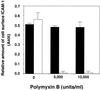
Lipoproteins in the cell membranes of both Mycoplasma salivarium and Mycoplasma fermentans were demonstrated to trigger the transcription of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 mRNA in normal fibroblasts isolated from human gingival tissue and to induce its cell surface expression by a mechanism distinct from that of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. The lipid moiety of the lipoproteins was suggested to play a key role in the expression of the activity.
Figures


References
-
- Chingbingyong M I, Huges C V. Detection of Mycoplasma fermentans in human saliva with polymerase chain reaction-based assay. Arch Oral Biol. 1997;41:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Crawford J M. Distribution of ICAM-1, LFA-3 and HLA-DR in healthy and diseased gingival tissues. J Periodontal Res. 1992;27:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Diamond M S, Staunton D E, Marlin S D, Springer T A. Binding of the integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) to the third immunoglobulin-like domain of ICAM-1 (CD54) and its regulation by glycosylation. Cell. 1991;65:961–971. - PubMed
-
- Dully J R, Grieve P A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975;64:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Dustin M L, Rothlein R, Bhan A K, Dinarello C A, Springer T A. Induction by IL-1 and interferon-γ: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1) J Immunol. 1986;137:245–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

