The SRm160/300 splicing coactivator is required for exon-enhancer function
- PMID: 10339552
- PMCID: PMC26846
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6125
The SRm160/300 splicing coactivator is required for exon-enhancer function
Abstract
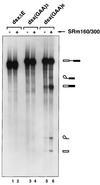
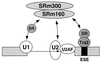
Exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) sequences are important for the recognition of splice sites in pre-mRNA. These sequences are bound by specific serine-arginine (SR) repeat proteins that promote the assembly of splicing complexes at adjacent splice sites. We have recently identified a splicing "coactivator," SRm160/300, which contains SRm160 (the SR nuclear matrix protein of 160 kDa) and a 300-kDa nuclear matrix antigen. In the present study, we show that SRm160/300 is required for a purine-rich ESE to promote the splicing of a pre-mRNA derived from the Drosophila doublesex gene. The association of SRm160/300 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) with this pre-mRNA requires both U1 snRNP and factors bound to the ESE. Independently of pre-mRNA, SRm160/300 specifically interacts with U2 snRNP and with a human homolog of the Drosophila alternative splicing regulator Transformer 2, which binds to purine-rich ESEs. The results suggest a model for ESE function in which the SRm160/300 splicing coactivator promotes critical interactions between ESE-bound "activators" and the snRNP machinery of the spliceosome.
Figures
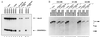
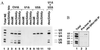

References
-
- Burge C B, Tuschl T, Sharp P A. In: The RNA World. 2nd Ed. Gesteland R F, Cech T R, Atkins J F, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1999. pp. 525–560.
-
- Kramer A. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:367–409. - PubMed
-
- Valcarcel J, Green M R. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:296–301. - PubMed
-
- Manley J, Tacke R. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1569–1579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

