Inhibition of RNase P RNA cleavage by aminoglycosides
- PMID: 10339557
- PMCID: PMC26851
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6155
Inhibition of RNase P RNA cleavage by aminoglycosides
Abstract
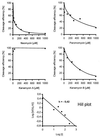
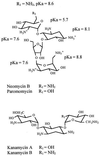
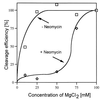
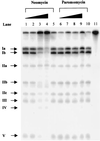
A number of aminoglycosides have been reported to interact and interfere with the function of various RNA molecules. Among these are 16S rRNA, the group I intron, and the hammerhead ribozymes. In this report we show that cleavage by RNase P RNA in the absence as well as in the presence of the RNase P protein is inhibited by several aminoglycosides. Among the ones we tested, neomycin B was found to be the strongest inhibitor with a Ki value in the micromolar range (35 microM). Studies of lead(II)-induced cleavage of RNase P RNA suggested that binding of neomycin B interfered with the binding of divalent metal ions to the RNA. Taken together, our findings suggest that aminoglycosides compete with Mg2+ ions for functionally important divalent metal ion binding sites. Thus, RNase P, which is an essential enzyme, is indeed a potential drug target that can be used to develop new drugs by using various aminoglycosides as lead compounds.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of eukaryotic ribonuclease P activity by aminoglycosides: kinetic studies.FEBS Lett. 2000 Nov 17;485(1):71-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02190-6. FEBS Lett. 2000. PMID: 11086168
-
Manganese ions induce miscleavage in the Escherichia coli RNase P RNA-catalyzed reaction.J Mol Biol. 1999 Sep 10;292(1):53-63. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3048. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10493856
-
NAIM and site-specific functional group modification analysis of RNase P RNA: magnesium dependent structure within the conserved P1-P4 multihelix junction contributes to catalysis.Biochemistry. 2002 Apr 9;41(14):4533-45. doi: 10.1021/bi012158h. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 11926814
-
RNase P RNA of Mycoplasma capricolum.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):125-9. doi: 10.1007/BF00988716. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901498 Review.
-
Recent approaches to probe functional groups in ribonuclease P RNA by modification interference.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):161-9. doi: 10.1007/BF00988723. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901505 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus RnpA.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Apr 28;8(2):48. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8020048. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31035380 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of HIV TAR RNA by triazole linked neomycin dimers.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Aug 15;21(16):4788-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.06.058. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21757341 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoglycoside Enhances the Delivery of Antisense Morpholino Oligonucleotides In Vitro and in mdx Mice.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Jun 7;16:663-674. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.04.023. Epub 2019 May 2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31121478 Free PMC article.
-
A screening platform to monitor RNA processing and protein-RNA interactions in ribonuclease P uncovers a small molecule inhibitor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6425-6438. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz285. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30997498 Free PMC article.
-
A Riboswitch-Driven Era of New Antibacterials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 13;11(9):1243. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091243. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

