Regulation of the OxyR transcription factor by hydrogen peroxide and the cellular thiol-disulfide status
- PMID: 10339558
- PMCID: PMC26852
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6161
Regulation of the OxyR transcription factor by hydrogen peroxide and the cellular thiol-disulfide status
Abstract
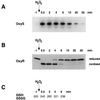
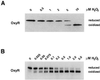
The Escherichia coli transcription factor OxyR is activated by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond and subsequently is deactivated by enzymatic reduction of the disulfide bond. Here we show that OxyR can be activated by two possible pathways. In mutants defective in the cellular disulfide-reducing systems, OxyR is constitutively activated by a change in the thiol-disulfide redox status in the absence of added oxidants. In wild-type cells, OxyR is activated by hydrogen peroxide. By monitoring the presence of the OxyR disulfide bond after exposure to hydrogen peroxide in vivo and in vitro, we also show that the kinetics of OxyR oxidation by low concentrations of hydrogen peroxide is significantly faster than the kinetics of OxyR reduction, allowing for transient activation in an overall reducing environment. We propose that the activity of OxyR in vivo is determined by the balance between hydrogen peroxide levels and the cellular redox environment.
Figures


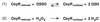
References
-
- Zheng M, Åslund F, Storz G. Science. 1998;279:1718–1721. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert H F. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:69–172. - PubMed
-
- Holmgren A, Fagerstedt M. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:6926–6930. - PubMed
-
- Hwang C, Sinskey A J, Lodish H F. Science. 1992;257:1496–1502. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

