The natural killer gene complex genetic locus Chok encodes Ly-49D, a target recognition receptor that activates natural killing
- PMID: 10339587
- PMCID: PMC26881
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6330
The natural killer gene complex genetic locus Chok encodes Ly-49D, a target recognition receptor that activates natural killing
Abstract
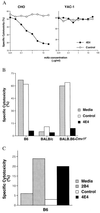
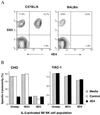
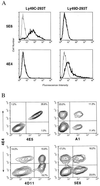
Previously, we established that natural killer (NK) cells from C57BL/6 (B6), but not BALB/c, mice lysed Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, and we mapped the locus that determines this differential CHO-killing capacity to the NK gene complex on chromosome 6. The localization of Chok in the NK gene complex suggested that it may encode either an activating or an inhibitory receptor. Here, results from a lectin-facilitated lysis assay predicted that Chok is an activating B6 NK receptor. Therefore, we immunized BALB/c mice with NK cells from BALB.B6-Cmv1(r) congenic mice and generated a mAb, designated 4E4, that blocked B6-mediated CHO lysis. mAb 4E4 also redirected lysis of Daudi targets, indicating its reactivity with an activating NK cell receptor. Furthermore, only the 4E4(+) B6 NK cell subset mediated CHO killing, and this lysis was abrogated by preincubation with mAb 4E4. Flow cytometric analysis indicated that mAb 4E4 specifically reacts with Ly-49D but not Ly-49A, B, C, E, G, H, or I transfectants. Finally, gene transfer of Ly-49DB6 into BALB/c NK cells conferred cytotoxic capacity against CHO cells, thus establishing that the Ly-49D receptor is sufficient to activate NK cells to lyse this target. Hence, Ly-49D is the Chok gene product and is a mouse NK cell receptor capable of directly triggering natural killing.
Figures


References
-
- Brown M G, Fulmek S, Matsumoto K, Cho R, Lyons P A, Levy E R, Scalzo A A, Yokoyama W M. Genomics. 1997;42:16–25. - PubMed
-
- Vance R E, Tanamachi D M, Hanke T, Raulet D H. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:3236–3241. - PubMed
-
- Karlhofer F M, Ribaudo R K, Yokoyama W M. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1992;105:72–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

