Sustained hypersensitivity to angiotensin II and its mechanism in mice lacking the subtype-2 (AT2) angiotensin receptor
- PMID: 10339618
- PMCID: PMC26912
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6506
Sustained hypersensitivity to angiotensin II and its mechanism in mice lacking the subtype-2 (AT2) angiotensin receptor
Abstract
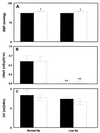
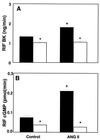
The vast majority of the known biological effects of the renin-angiotensin system are mediated by the type-1 (AT1) receptor, and the functions of the type-2 (AT2) receptor are largely unknown. We investigated the role of the AT2 receptor in the vascular and renal responses to physiological increases in angiotensin II (ANG II) in mice with targeted deletion of the AT2 receptor gene. Mice lacking the AT2 receptor (AT2-null mice) had slightly elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) compared with that of wild-type (WT) control mice (P < 0.0001). In AT2-null mice, infusion of ANG II (4 pmol/kg/min) for 7 days produced a marked and sustained increase in SBP [from 116 +/- 0.5 to 208 +/- 1 mmHg (P < 0.0001) (1 mmHg = 133 Pa)] and reduction in urinary sodium excretion (UNaV) [from 0.6 +/- 0.01 to 0.05 +/- 0.002 mM/day (P < 0.0001)] whereas neither SBP nor UNaV changed in WT mice. AT2-null mice had low basal levels of renal interstitial fluid bradykinin (BK), and cyclic guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate, an index of nitric oxide production, compared with WT mice. In WT mice, dietary sodium restriction or ANG II infusion increased renal interstitial fluid BK, and cyclic guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate by approximately 4-fold (P < 0.0001) whereas no changes were observed in AT2-null mice. These results demonstrate that the AT2 receptor is necessary for normal physiological responses of BK and nitric oxide to ANG II. Absence of the AT2 receptor leads to vascular and renal hypersensitivity to ANG II, including sustained antinatriuresis and hypertension. These results strongly suggest that the AT2 receptor plays a counterregulatory protective role mediated via BK and nitric oxide against the antinatriuretic and pressor actions of ANG II.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

