Factors affecting counteraction by methylamines of urea effects on aldose reductase
- PMID: 10339620
- PMCID: PMC26914
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6517
Factors affecting counteraction by methylamines of urea effects on aldose reductase
Abstract
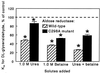
The concentration of urea in renal medullary cells is high enough to affect enzymes seriously by reducing Vmax or raising Km, yet the cells survive and function. The usual explanation is that the methylamines found in the renal medulla, namely glycerophosphocholine and betaine, have actions opposite to those of urea and thus counteract its effects. However, urea and methylamines have the similar (not counteracting) effects of reducing both the Km and Vmax of aldose reductase (EC 1.1.1.21), an enzyme whose function is important in renal medullas. Therefore, we examined factors that might determine whether counteraction occurs, namely different combinations of assay conditions (pH and salt concentration), methylamines (glycerophosphocholine, betaine, and trimethylamine N-oxide), substrates (DL-glyceraldehyde and D-xylose), and a mutation in recombinant aldose reductase protein (C298A). We find that Vmax of both wild-type and C298A mutant generally is reduced by urea and/or the methylamines. However, the effects on Km are much more complex, varying widely with the combination of conditions. At one extreme, we find a reduction of Km of wild-type enzyme by urea and/or methylamines that is partially additive, whereas at the other extreme we find that urea raises Km for D-xylose of the C298A mutant, betaine lowers the Km, and the two counteract in a classical fashion so that at a 2:1 molar ratio of betaine to urea there is no net effect. We conclude that counteraction of urea effects on enzymes by methylamines can depend on ion concentration, pH, the specific methylamine and substrate, and identity of even a single amino acid in the enzyme.
Figures




References
-
- Yancey P H, Somero G N. J Exp Zool. 1980;212:205–213.
-
- Bagnasco S, Balaban R, Fales H M, Yang Y M, Burg M. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:5872–5877. - PubMed
-
- Lin T Y, Timasheff S N. Biochemistry. 1994;33:12695–12701. - PubMed
-
- Yancey P H, Clark M E, Hand S C, Bowlus R D, Somero G N. Science. 1982;217:1214–1222. - PubMed
-
- Yancey P H, Burg M B. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:R198–R204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

