Cloning and characterization of Aplysia neutral endopeptidase, a metallo-endopeptidase involved in the extracellular metabolism of neuropeptides in Aplysia californica
- PMID: 10341232
- PMCID: PMC6782589
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-11-04280.1999
Cloning and characterization of Aplysia neutral endopeptidase, a metallo-endopeptidase involved in the extracellular metabolism of neuropeptides in Aplysia californica
Abstract
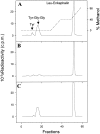
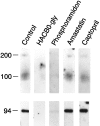
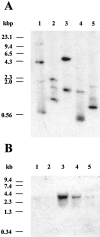
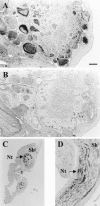
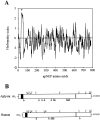
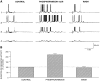
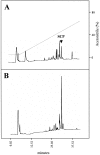
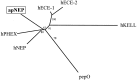
Cell surface metallo-endopeptidases play important roles in cell communication by controlling the levels of bioactive peptides around peptide receptors. To understand the relative relevance of these enzymes in the CNS, we characterized a metallo-endopeptidase in the CNS of Aplysia californica, whose peptidergic pathways are well described at the molecular, cellular, and physiological levels. The membrane-bound activity cleaved Leu-enkephalin at the Gly3-Phe4 bond with an inhibitor profile similar to that of the mammalian neutral endopeptidase (NEP). This functional homology was supported by the molecular cloning of cDNAs from the CNS, which demonstrated that the Aplysia and mammalian NEPs share all the same amino acids that are essential for the enzymatic activity. The protein is recognized both by specific anti-Aplysia NEP (apNEP) antibodies and by the [125I]-labeled NEP-specific inhibitor RB104, demonstrating that the apNEP gene codes for the RB104-binding protein. In situ hybridization experiments on sections of the ganglia of the CNS revealed that apNEP is expressed in neurons and that the mRNA is present both in the cell bodies and in neurites that travel along the neuropil and peripheral nerves. When incubated in the presence of a specific NEP inhibitor, many neurons of the buccal ganglion showed a greatly prolonged physiological response to stimulation, suggesting that NEP-like metallo-endopeptidases may play a critical role in the regulation of the feeding behavior in Aplysia. One of the putative targets of apNEP in this behavior is the small cardioactive peptide, as suggested by RP-HPLC experiments. More generally, the presence of apNEP in the CNS and periphery may indicate that it could play a major role in the modulation of synaptic transmission in Aplysia and in the metabolism of neuropeptides close to their point of release.
Figures

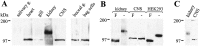
References
-
- Almenoff J, Teirstein AS, Thornton JC, Orlowski M. Identification of a thermolysin-like metallo-endopeptidase in serum: activity in normal subjects and in patients with sarcoidosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1984;103:420–431. - PubMed
-
- Auclair D, Lang BF, Forest P, DesGroseillers L. Analysis of genes encoding highly conserved lysine-rich proteins in Aplysia californica and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1994;220:997–1003. - PubMed
-
- Barnes K, Turner AJ, Kenny AJ. Electromicroscopic immunocytochemistry of pig brain shows that endopeptidase-24.11 is localized in neuronal membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1988;94:64–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
