Role of phosphorylation of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein during neuronal differentiation
- PMID: 10341243
- PMCID: PMC6782598
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-11-04421.1999
Role of phosphorylation of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein during neuronal differentiation
Abstract
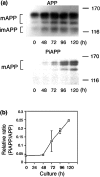
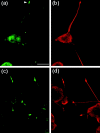
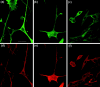
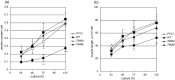
Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein (APP), the precursor of beta-amyloid (Abeta), is an integral membrane protein with a receptor-like structure. We recently demonstrated that the mature APP (mAPP; N- and O-glycosylated form) is phosphorylated at Thr668 (numbering for APP695 isoform), specifically in neurons. Phosphorylation of mAPP appears to occur during, and after, neuronal differentiation. Here we report that the phosphorylation of mAPP begins 48-72 hr after treatment of PC12 cells with NGF and that this correlates with the timing of neurite outgrowth. The phosphorylated form of APP is distributed in neurites and mostly in the growth cones of differentiating PC12 cells. PC12 cells stably expressing APP with Thr668Glu substitution showed remarkably reduced neurite extension after treatment with NGF. These observations suggest that the phosphorylated form of APP may play an important role in neurite outgrowth of differentiating neurons.
Figures

References
-
- Beher D, Hesse L, Masters CL, Multhaup G. Regulation of amyloid protein precursor (APP) binding to collagen and mapping of the binding sites on APP and collagen type 1. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1613–1620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
