Immunohistochemical evidence of seizure-induced activation of trk receptors in the mossy fiber pathway of adult rat hippocampus
- PMID: 10341259
- PMCID: PMC6782602
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-11-04616.1999
Immunohistochemical evidence of seizure-induced activation of trk receptors in the mossy fiber pathway of adult rat hippocampus
Abstract
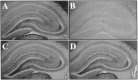
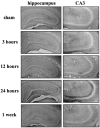
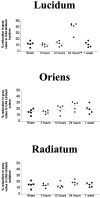
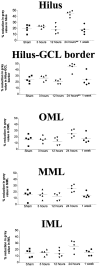
Recent work suggests that limiting the activation of the trkB subtype of neurotrophin receptor inhibits epileptogenesis, but whether or where neurotrophin receptor activation occurs during epileptogenesis is unclear. Because the activation of trk receptors involves the phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues, the availability of antibodies that selectively recognize the phosphorylated form of trk receptors permits a histochemical assessment of trk receptor activation. In this study the anatomy and time course of trk receptor activation during epileptogenesis were assessed with immunohistochemistry, using a phospho-specific trk antibody. In contrast to the low level of phosphotrk immunoreactivity constitutively expressed in the hippocampus of adult rats, a striking induction of phosphotrk immunoreactivity was evident in the distribution of the mossy fibers after partial kindling or kainate-induced seizures. The anatomic distribution, time course, and threshold for seizure-induced phosphotrk immunoreactivity correspond to the demonstrated pattern of regulation of BDNF expression by seizure activity. These results provide immunohistochemical evidence that trk receptors undergo activation during epileptogenesis and suggest that the mossy fiber pathway is particularly important in the pro-epileptogenic effects of the neurotrophins.
Figures


References
-
- Barbacid M. The trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol. 1994;25:1386–1403. - PubMed
-
- Behr J, Lyson KJ, Mody I. Enhanced propagation of epileptiform activity through the kindled dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:1726–1732. - PubMed
-
- Bengzon J, Soderstrom S, Kokaia Z, Kokaia M, Ernfors P, Persson H, Ebendal T, Lindvall O. Widespread increase of nerve growth factor protein in the rat forebrain after kindling-induced seizures. Brain Res. 1992;587:338–342. - PubMed
-
- Bengzon J, Kokaia Z, Ernfors P, Kokaia M, Leanza G, Nilsson OG, Persson H, Lindvall O. Regulation of neurotrophin and trkA, trkB, and trkC tyrosine kinase receptor messenger RNA expression in kindling. Neuroscience. 1993;53:433–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
