Influence of sulphasalazine, methotrexate, and the combination of both on plasma homocysteine concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 10343521
- PMCID: PMC1752831
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.2.79
Influence of sulphasalazine, methotrexate, and the combination of both on plasma homocysteine concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To study the influence of sulphasalazine (SSZ), methotrexate (MTX), and the combination (COMBI) of both on plasma homocysteine and to study the relation between plasma homocysteine and their clinical effects.
Methods: 105 patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were randomised between SSZ (2-3 g/day), MTX (7.5-15 mg/week), and the COMBI (same dose range) and evaluated double blindly during 52 weeks. Plasma homocysteine, serum folate concentrations, and vitamin B12 were measured. The influence of the C677T mutation of the enzyme methyl-enetetrahydrofolatereductase (MTHFR) gene was analysed.
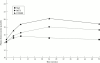
Results: A slight trend towards increased efficacy and an increased occurrence of minor gastrointestinal toxicity was present in the COMBI group, no differences existed clinically between SSZ and MTX. Only a slight and temporary increase in plasma homocysteine was found in the SSZ group, in contrast with the persistent rise in the MTX group and the even greater increase in the COMBI patients. Patients homozygous for the mutation in the MTHFR gene had significantly higher baseline homocysteine, heterozygous MTHFR genotype induced a significantly higher plasma homoeysteine at week 52 compared with no mutation. No correlation was found between clinical efficacy variables and homocysteine. Patients with gastrointestinal toxicity had a significantly greater increase in homocysteine.
Conclusion: A persistent increase in plasma homocysteine concentrations was observed in patients treated with MTX alone and more pronounced in combination with SSZ, in contrast with SSZ alone. An increase in plasma homocysteine is related to the C677T mutation in MTHFR. A relation in the change in homocysteine concentrations with (gastrointestinal) toxicity was found, no relation with clinical efficacy existed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homocysteine and folate status in methotrexate-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002 Jun;41(6):658-65. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.6.658. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002. PMID: 12048292 Clinical Trial.
-
Combination of sulphasalazine and methotrexate versus the single components in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind, 52 week clinical trial.Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Oct;36(10):1082-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.10.1082. Br J Rheumatol. 1997. PMID: 9374925 Clinical Trial.
-
The C677T mutation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene: a genetic risk factor for methotrexate-related elevation of liver enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Nov;44(11):2525-30. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2525::aid-art432>3.0.co;2-b. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11710708 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of hyperhomocysteinemia with genetic variants in key enzymes of homocysteine metabolism and methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Inflamm Res. 2018 Aug;67(8):703-710. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1161-8. Epub 2018 May 23. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29796841
-
Associations between the C677T and A1298C polymorphisms of MTHFR and the efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis.Clin Drug Investig. 2010;30(2):101-8. doi: 10.2165/11531070-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2010. PMID: 20067328 Review.
Cited by
-
[Reducing toxicity of methotrexate with folic acid].Z Rheumatol. 2005 Jun;64(5):353-8. doi: 10.1007/s00393-005-0638-3. Z Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 15965822 German.
-
Gene polymorphisms and pharmacogenetics in rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Genomics. 2008 Sep;9(6):381-93. doi: 10.2174/138920208785699553. Curr Genomics. 2008. PMID: 19506728 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between methotrexate treatment and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms with incident fractures in Japanese female rheumatoid arthritis patients.J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(5):574-83. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0073-7. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009. PMID: 19333678
-
Therapeutic potential of folic acid supplementation for cardiovascular disease prevention through homocysteine lowering and blockade in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Biomark Res. 2015 Sep 4;3:24. doi: 10.1186/s40364-015-0049-9. eCollection 2015. Biomark Res. 2015. PMID: 26346508 Free PMC article.
-
Management of cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: evidence and expert opinion.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013 Aug;5(4):166-81. doi: 10.1177/1759720X13491025. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013. PMID: 23904862 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

