Destruction of articular cartilage by alpha 2 macroglobulin elastase complexes: role in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 10343526
- PMCID: PMC1752824
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.2.109
Destruction of articular cartilage by alpha 2 macroglobulin elastase complexes: role in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Neutrophil elastase accounts for the ability of some fresh rheumatoid synovial fluids to degrade cartilage matrix in vitro. The aim of this study was to determine if enzyme activity could result from depletion of synovial fluid inhibitors or protection of the enzyme from inhibition.
Methods: The ability of synovial fluids to inhibit porcine pancreatic elastase was investigated together with chemical pretreatments capable of inactivating alpha 1 protease inhibitor (alpha 1PI) or preventing formation of alpha 2 macroglobulin (alpha 2M) elastase complexes. Subsequently, complexes of human neutrophil elastase with alpha 2M were prepared and applied to frozen sections of cartilage. Proteoglycan loss was quantified by alcian blue staining and scanning and integrating microdensitometry. Parallel studies were carried out using a low molecular weight chromogenic elastase substrate. The effects of alpha 1PI and SF on these systems were investigated. Finally, synovial fluids were subjected to gel filtration and the fractions assayed for elastase activity. High molecular weight fractions were pooled, concentrated, and tested for their ability to degrade cartilage sections.
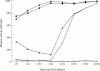
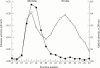
Results: All synovial fluids reduced the activity of porcine pancreatic elastase, the inhibition mainly being attributable to alpha 1PI, whereas remaining activity resulted from complexes of elastase with alpha 2M. Complexes of human neutrophil elastase with alpha 2M were shown to cause proteoglycan degradation in frozen sections of human articular cartilage. Alpha 1PI prevented alpha 2M elastase complexes from degrading cartilage but not the chromogenic substrate. The data suggested that alpha 1PI does not inhibit elastase bound to alpha 2M but sterically hinders the complex. However, only one of five synovial fluids was able to completely block the actions of alpha 2M elastase complexes against cartilage. Gel filtration of rheumatoid synovial fluids showed elastase and cartilage degrading activity to be associated with fractions that contained alpha 2M, and not with fractions expected to contain free enzyme.
Conclusions: The data suggest that synovial fluid alpha 2M elastase complexes can degrade cartilage matrix in rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complexes as correlated with alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor-elastase complexes in synovial fluids of rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):319-25. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290303. Arthritis Rheum. 1986. PMID: 2421737
-
Impaired activity of protease inhibitors towards neutrophil elastase bound to human articular cartilage.Ann Rheum Dis. 1996 Apr;55(4):248-52. doi: 10.1136/ard.55.4.248. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996. PMID: 8733442 Free PMC article.
-
Predominant role of neutrophils in the inactivation of alpha 2-macroglobulin in arthritic joints.Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1139-50. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340910. Arthritis Rheum. 1991. PMID: 1718287
-
Intraarticular alpha 2-macroglobulin complexes and proteolytic activity in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.Pediatr Res. 1993 Aug;34(2):204-7. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199308000-00021. Pediatr Res. 1993. PMID: 7694228
-
Biochemistry of articular cartilage in rheumatic diseases.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1980;38:25-9. doi: 10.3109/03009748109096711. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1980. PMID: 7010575 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Proteinases and their receptors in inflammatory arthritis: an overview.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;14(3):170-180. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2018.17. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29416136 Review.
-
Alpha-2-Macroglobulin in Inflammation, Immunity and Infections.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:803244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.803244. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Synovial Fluid Enzymes on the Biodegradability of Collagen and Fibrin Clots.Materials (Basel). 2011 Aug 20;4(8):1469-1482. doi: 10.3390/ma4081469. Materials (Basel). 2011. PMID: 21949586 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma apolipoprotein(a) co-deposits with fibrin in inflammatory arthritic joints.Am J Pathol. 2001 Oct;159(4):1445-53. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62531-X. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11583972 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolysis and Deficiency of α1-Proteinase Inhibitor in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biochem Mosc Suppl B Biomed Chem. 2022;16(4):271-291. doi: 10.1134/S1990750822040035. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Biochem Mosc Suppl B Biomed Chem. 2022. PMID: 36407837 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

