Thrombin receptor mediated signals induce expressions of interleukin 6 and granulocyte colony stimulating factor via NF-kappa B activation in synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 10343541
- PMCID: PMC1752754
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.1.55
Thrombin receptor mediated signals induce expressions of interleukin 6 and granulocyte colony stimulating factor via NF-kappa B activation in synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
Objective: To clarify the mechanism of thrombin receptor mediated signal transduction and the induction of cytokines by thrombin stimulation in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.
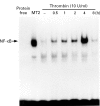
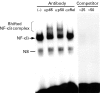
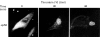
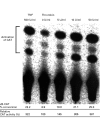
Methods: Cytokines were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the supernatants of cultured rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts stimulated by thrombin. To assess the mechanism of thrombin receptor mediated signal transduction in the rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts, electrophoretic mobility gel shift assay (EMSA), immunoglobulin kappa-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) assay, and immunostaining for NF-kappa B subunit molecule was performed.
Results: Thrombin stimulation activated the inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B, and then induced subsequent expressions of interleukin 6 (IL6) and granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in the cells.
Conclusion: Thrombin receptor mediated signal transduction could induce the expressions of IL6 and G-CSF, and increase inflammatory events in the cavum articulare via NF-kappa B activation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

