Nbs1 potentiates ATP-driven DNA unwinding and endonuclease cleavage by the Mre11/Rad50 complex
- PMID: 10346816
- PMCID: PMC316715
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.10.1276
Nbs1 potentiates ATP-driven DNA unwinding and endonuclease cleavage by the Mre11/Rad50 complex
Abstract
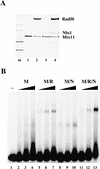
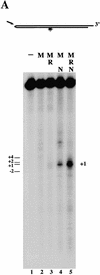
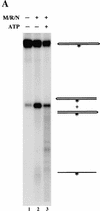
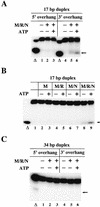
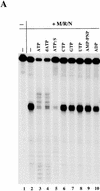
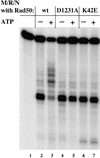
The Nijmegen breakage syndrome gene product (Nbs1) was shown recently to associate in vivo with the Mre11 and Rad50 proteins, which play pivotal roles in eukaryotic DNA double-strand break repair, meiotic recombination, and telomere maintenance. We show in this work that the triple complex of recombinant Nbs1, Mre11, and Rad50 proteins binds cooperatively to DNA and forms a distinct protein-DNA species. The Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex displays several enzymatic activities that are not seen without Nbs1, including partial unwinding of a DNA duplex and efficient cleavage of fully paired hairpins. Unwinding and hairpin cleavage are both increased by the presence of ATP. On nonhairpin DNA ends, ATP controls a switch in endonuclease specificity that allows Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 to cleave a 3'-protruding strand at a double-/single-strand transition. Mutational analysis demonstrates that Rad50 is responsible for ATP binding by the complex, but the ATP-dependent activities are expressed only with Nbs1 present.
Figures






References
-
- Alani E, Padmore R, Kleckner N. Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell. 1990;61:419–436. - PubMed
-
- Besmer E, Mansilla-Soto J, Cassard S, Sawchuk DJ, Brown G, Sadofsky M, Lewis SM, Nussenzweig MC, Cortes P. Hairpin coding end opening is mediated by RAG1 and RAG2 proteins. Mol Cell. 1998;2:817–828. - PubMed
-
- Bianco PR, Tracy RB, Kowalczykowski SC. DNA strand exchange proteins: A biochemical and physical comparison. Front Biosci. 1998;3:d570–d603. - PubMed
-
- Bork P, Hofmann K, Bucher P, Neuwald AF, Altschul SF, Koonin EV. A superfamily of conserved domains in DNA damage-responsive cell cycle checkpoint proteins. FASEB J. 1997;11:68–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
