Chemoselective nitro group reduction and reductive dechlorination initiate degradation of 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol by Ralstonia eutropha JMP134
- PMID: 10347008
- PMCID: PMC91343
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.6.2317-2323.1999
Chemoselective nitro group reduction and reductive dechlorination initiate degradation of 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol by Ralstonia eutropha JMP134
Abstract
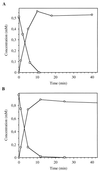
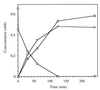
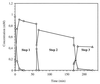
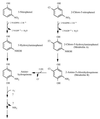
Ralstonia eutropha JMP134 utilizes 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol as a sole source of nitrogen, carbon, and energy. The initial steps for degradation of 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol are analogous to those of 3-nitrophenol degradation in R. eutropha JMP134. 2-Chloro-5-nitrophenol is initially reduced to 2-chloro-5-hydroxylaminophenol, which is subject to an enzymatic Bamberger rearrangement yielding 2-amino-5-chlorohydroquinone. The chlorine of 2-amino-5-chlorohydroquinone is removed by a reductive mechanism, and aminohydroquinone is formed. 2-Chloro-5-nitrophenol and 3-nitrophenol induce the expression of 3-nitrophenol nitroreductase, of 3-hydroxylaminophenol mutase, and of the dechlorinating activity. 3-Nitrophenol nitroreductase catalyzes chemoselective reduction of aromatic nitro groups to hydroxylamino groups in the presence of NADPH. 3-Nitrophenol nitroreductase is active with a variety of mono-, di-, and trinitroaromatic compounds, demonstrating a relaxed substrate specificity of the enzyme. Nitrosobenzene serves as a substrate for the enzyme and is converted faster than nitrobenzene.
Figures
References
-
- Anlezark G M, Melton R G, Sherwood R F, Coles B, Friedlos F, Knox R. The bioactivation of 5-(aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide (CB1954)-1. Purification and properties of a nitroreductase enzyme from Escherichia coli—a potential enzyme for antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;44:2289–2295. - PubMed
-
- Balajee S, Mahadevan A. Dissimilation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by Azotobacter chrococcum. Xenobiotica. 1990;20:607–617. - PubMed
-
- Becker A R, Sternson L A. Nonenzymatic reduction of nitrosobenzene to phenylhydroxylamine by NAD(P)H. Bioorg Chem. 1980;9:305–312.
-
- Beunink J, Rehm H-J. Coupled reductive and oxidative degradation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by a co-immobilized mixed culture system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990;34:108–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

