ACTG 260: a randomized, phase I-II, dose-ranging trial of the anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity of delavirdine monotherapy. The AIDS Clinical Trials Group Protocol 260 Team
- PMID: 10348755
- PMCID: PMC89281
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.6.1373
ACTG 260: a randomized, phase I-II, dose-ranging trial of the anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity of delavirdine monotherapy. The AIDS Clinical Trials Group Protocol 260 Team
Abstract
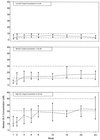
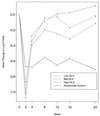
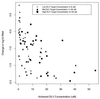
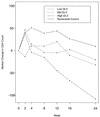
ACTG 260 was an open-label, four-arm trial designed to study the safety and anti-human immunodeficiency virus (anti-HIV) activity of delavirdine monotherapy at three ranges of concentrations in plasma compared to those of control therapy with zidovudine or didanosine. Delavirdine doses were adjusted weekly until subjects were within their target trough concentration range (3 to 10, 11 to 30, or 31 to 50 microM). A total of 113 subjects were analyzed. At week 2, the mean HIV type 1 (HIV-1) RNA level declines among the subjects in the three delavirdine arms were similar (0.87, 1.08, and 1.02 log10 for the low, middle, and high target arms, respectively), but by week 8, the subjects in the pooled delavirdine arms showed only a 0.10 log10 reduction. In the subjects in the nucleoside arm, mean HIV-1 RNA level reductions at weeks 2 and 8 were 0.67 and 0.55 log10, respectively. Because viral suppression by delavirdine was not maintained, the trial was stopped early. Rash, which was usually self-limited, developed in 36% of subjects who received delavirdine. Delavirdine monotherapy has potent anti-HIV activity at 2 weeks, but its activity is time limited due to the rapid emergence of drug resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delavirdine: a review of its use in HIV infection.Drugs. 2000 Dec;60(6):1411-44. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200060060-00013. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11152019 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of delavirdine mesylate with zidovudine and didanosine compared with two-drug combinations of these agents in persons with HIV disease with CD4 counts of 100 to 500 cells/mm3 (ACTG 261). ACTG 261 Team.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999 Aug 1;21(4):281-92. doi: 10.1097/00126334-199908010-00005. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999. PMID: 10428106 Clinical Trial.
-
Continued lamivudine versus delavirdine in combination with indinavir and zidovudine or stavudine in lamivudine-experienced patients: results of Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group protocol 370.AIDS. 2000 Jul 28;14(11):1553-61. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200007280-00011. AIDS. 2000. PMID: 10983642 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical experience with adding delavirdine to combination therapy in patients in whom multiple antiretroviral treatment including protease inhibitors has failed.AIDS. 1998 Jul 30;12(11):1333-40. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199811000-00015. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9708413
-
Delavirdine.2017 Dec 27. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2017 Dec 27. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643235 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Delavirdine in combination with zidovudine in treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients: evaluation of efficacy and emergence of viral resistance in a randomized, comparative phase III trial. The M/3331/0013B Study Group.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Nov;44(11):3155-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.11.3155-3157.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 11036040 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mutants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase resistant to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors demonstrate altered rates of RNase H cleavage that correlate with HIV-1 replication fitness in cell culture.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(18):8390-401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8390-8401.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10954539 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Food on the Steady-State Pharmacokinetics of Delavirdine in Patients with HIV Infection.Clin Drug Investig. 2003;23(4):255-61. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200323040-00005. Clin Drug Investig. 2003. PMID: 17535038
-
Multiple-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Delavirdine Mesylate and Didanosine in HIV-Infected Patients.Clin Drug Investig. 2003;23(5):323-8. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200323050-00002. Clin Drug Investig. 2003. PMID: 17535044
-
Delavirdine: a review of its use in HIV infection.Drugs. 2000 Dec;60(6):1411-44. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200060060-00013. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11152019 Review.
References
-
- D’Aquila R T, Hughes M D, Johnson V A, Fischl M A, Sommadossi J P, Liou S, Timpone J, Myers M, Basgoz N, Niu M, Hirsh M S. Nevirapine, zidovudine, and didanosine compared to zidovudine, and didanosine in patients with HIV-1 infection. Ann Intern Med. 1996;1214:1019–1030. - PubMed
-
- Davey R T, Chaitt D G, Reed G F, Freimuth W W, Herpin B R, Metcalf J A, Eastman P S, Falloon J, Kovacs J A, Polis M A, Walker R E, Masur H, Boyle J, Coleman S, Cox S R, Wathen L, Daenzer C L, Lane H C. Randomized, controlled phase I/II trial of combination therapy with delavirdine (U-90152S) and conventional nucleosides in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40:1657–1664. - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeJong M D, Vella S, Carr A, et al. High-dose nevirapine in previously untreated human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infected persons does not result in sustained suppression of viral replication. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:966–970. - PubMed
-
- Demeter L, Shafer R, Para M, Morse G, Freimuth W, Merigan T, Reichman R. Program and abstracts of the Third Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections. 1996. Delavirdine susceptibility of HIV-1 isolates obtained from patients receiving delavirdine monotherapy-ACTG 260, abstr. 322; p. 113.
-
- Dueweke T L, Kezdy F J, Waszak G A, Deibel M R, Tarpley W G. The binding of a novel bisheteroarylpiperazine mediates inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:27–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

