In vitro anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities of Z- and E-methylenecyclopropane nucleoside analogues and their phosphoro-L-alaninate diesters
- PMID: 10348777
- PMCID: PMC89303
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.6.1487
In vitro anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities of Z- and E-methylenecyclopropane nucleoside analogues and their phosphoro-L-alaninate diesters
Abstract
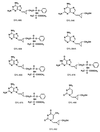
Nucleoside analogues with a Z- or an E-methylenecyclopropane moiety were synthesized and examined for activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in vitro. The addition of a methyl phenyl phosphoro-L-alaninate moiety to modestly active analogues resulted in potentiation of their anti-HIV-1 activity. Two such compounds, designated QYL-685 (with 2,6-diaminopurine) and QYL-609 (with adenine), were most potent against HIV-1 in vitro, with 50% inhibitory concentrations of 0.034 and 0.0026 microM, respectively, in MT-2 cell-based assays. Both compounds were active against zidovudine-resistant, didanosine-resistant, and multi-dideoxynucleoside-resistant infectious clones in vitro. Further development of these analogues as potential therapies for HIV-1 infection is warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro induction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants resistant to phosphoralaninate prodrugs of Z-methylenecyclopropane nucleoside analogues.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Oct;43(10):2479-83. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.10.2479. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10508028 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antiviral activity of phosphoralaninate derivatives of methylenecyclopropane analogues of nucleosides.Antiviral Res. 1999 Aug;43(1):37-53. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(99)00029-7. Antiviral Res. 1999. PMID: 10480262
-
Synthesis and antiviral activity of (Z)- and (E)-2,2-[bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclopropylidene]methylpurines and -pyrimidines: second-generation methylenecyclopropane analogues of nucleosides.J Med Chem. 2004 Jan 29;47(3):566-75. doi: 10.1021/jm030316s. J Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14736238
-
4'-C-substituted-2'-deoxynucleosides: a family of antiretroviral agents which are potent against drug-resistant HIV variants.Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2001 May;1(1):1-10. doi: 10.2174/1568005013343218. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2001. PMID: 12455229 Review.
-
Structure, Synthesis and Inhibition Mechanism of Nucleoside Analogues as HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs).ChemMedChem. 2021 Mar 3;16(5):743-766. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000695. Epub 2021 Feb 9. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33230979 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of nucleoside phosphate and phosphonate prodrugs.Chem Rev. 2014 Sep 24;114(18):9154-218. doi: 10.1021/cr5002035. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 25144792 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
In vitro activities of methylenecyclopropane analogues of nucleosides and their phosphoralaninate prodrugs against cytomegalovirus and other herpesvirus infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Jun;44(6):1506-11. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.6.1506-1511.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10817700 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro induction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants resistant to phosphoralaninate prodrugs of Z-methylenecyclopropane nucleoside analogues.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Oct;43(10):2479-83. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.10.2479. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10508028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashton W T, Canning L F, Reynolds G F, Tolman R L, Karkas J D, Liou R, Davies M E, DeWitt C M, Perry H C, Field A K. Synthesis and antiherpetic activity of (S)-, (R)-, and (+/−)-9-[(2,3-dihydroxy-1-propoxy)methyl]guanine, linear isomers of 2′-nor-2′-deoxyguanosine. J Med Chem. 1985;28:926–933. - PubMed
-
- Ashton W T, Meurer L C, Cantone C L, Field A K, Hannah J, Karkas J D, Liou R, Patel G F, Perry H C, Wagner A F. Synthesis and antiherpetic activity of (+/−)-9-[[(Z)-2-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopropyl]methyl]guanine and related compounds. J Med Chem. 1988;31:2304–2315. - PubMed
-
- Barrish J C, Zahler R. Antiviral agents. Annu Rep Med Chem. 1993;28:131–140.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical