Growth phase-regulated induction of Salmonella-induced macrophage apoptosis correlates with transient expression of SPI-1 genes
- PMID: 10348855
- PMCID: PMC93810
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.11.3433-3437.1999
Growth phase-regulated induction of Salmonella-induced macrophage apoptosis correlates with transient expression of SPI-1 genes
Abstract
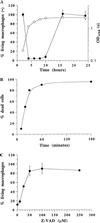
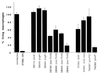
Invasive Salmonella has been reported to induce apoptosis in a fraction of infected macrophages within 2 to 14 h from the time of infection by a mechanism involving the type III secretion machinery encoded by the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1). Here, we show that bacteria in the transition from logarithmic to stationary phase cause 90% of the macrophages to undergo phagocytosis-independent, caspase-mediated apoptosis within 30 to 60 min of infection. The ability of Salmonella to induce this rapid apoptosis was growth phase regulated and cell type restricted, with epithelial cells being resistant. Apoptosis induction was also abrogated by disruption of the hilA gene (encoding a regulator of SPI-1 genes) and by the expression of a constitutively active PhoPQ. hilA itself and a subset of SPI-1 genes were transiently expressed during aerobic growth in liquid medium. Interestingly, however, hilA was found to be required only for the expression of the prgH gene, while sipB, invA, and invF were expressed in a hilA-independent manner. The expression of SPI-1 genes and the secretion of invasion-associated proteins correlated temporally with the induction of apoptosis and are likely to represent its molecular basis. Thus, growth phase transition regulates the expression and secretion of virulence determinants and represents the most efficient environmental cue for apoptosis induction reported to date.
Figures


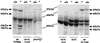
Similar articles
-
Derepression of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 genes within macrophages leads to rapid apoptosis via caspase-1- and caspase-3-dependent pathways.Cell Microbiol. 2005 Jan;7(1):79-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00435.x. Cell Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15617525
-
The Small RNA PinT Contributes to PhoP-Mediated Regulation of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Sep 6;201(19):e00312-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00312-19. Print 2019 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31262841 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of Salmonella typhimurium type III secreted proteins by pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1)-encoded transcriptional activators InvF and hilA.Infect Immun. 1999 Aug;67(8):4099-105. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.4099-4105.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10417179 Free PMC article.
-
The role of host cell death in Salmonella infections.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;289:131-50. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27320-4_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15791954 Review.
-
Genetic and environmental control of salmonella invasion.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:85-92. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765061 Review.
Cited by
-
sRNA-mediated RNA processing regulates bacterial cell division.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 9;49(12):7035-7052. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab491. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34125915 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium invasion genes by csrA.Infect Immun. 2000 Dec;68(12):6790-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6790-6797.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 11083797 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of 5 major Salmonella pathogenicity islands on NK cell depletion in mice infected with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Mar 12;10:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-75. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20226037 Free PMC article.
-
HilD induces expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 genes by displacing the global negative regulator H-NS from ssrAB.J Bacteriol. 2014 Nov;196(21):3746-55. doi: 10.1128/JB.01799-14. Epub 2014 Aug 18. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 25135218 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospira interrogans induces apoptosis in macrophages via caspase-8- and caspase-3-dependent pathways.Infect Immun. 2009 Feb;77(2):799-809. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00914-08. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19029301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bajaj V, Lucas R L, Hwang C, Lee C A. Coordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:703–714. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj V, Hwang C, Lee C A. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:715–727. - PubMed
-
- Chen L M, Kaniga K, Galán J E. Salmonella spp. are cytotoxic for cultured macrophages. Mol Microbiol. 1996;21:1101–1115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

