A functional 4-hydroxysalicylate/hydroxyquinol degradative pathway gene cluster is linked to the initial dibenzo-p-dioxin pathway genes in Sphingomonas sp. strain RW1
- PMID: 10348858
- PMCID: PMC93813
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.11.3452-3461.1999
A functional 4-hydroxysalicylate/hydroxyquinol degradative pathway gene cluster is linked to the initial dibenzo-p-dioxin pathway genes in Sphingomonas sp. strain RW1
Abstract
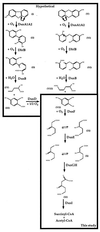
The bacterium Sphingomonas sp. strain RW1 is able to use dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran, and several hydroxylated derivatives as sole sources of carbon and energy. We have determined and analyzed the nucleic acid sequence of a 9,997-bp HindIII fragment downstream of cistrons dxnA1A2, which encode the dioxygenase component of the initial dioxygenase system of the corresponding catabolic pathways. This fragment contains 10 colinear open reading frames (ORFs), apparently organized in one compact operon. The enzymatic activities of some proteins encoded by these genes were analyzed in the strain RW1 and, after hyperexpression, in Escherichia coli. The first three ORFs of the locus, designated dxnC, ORF2, and fdx3, specify a protein with a low homology to bacterial siderophore receptors, a polypeptide representing no significant homology to known proteins, and a putative ferredoxin, respectively. dxnD encodes a 69-kDa phenol monooxygenase-like protein with activity for the turnover of 4-hydroxysalicylate, and dxnE codes for a 37-kDa protein whose sequence and activity are similar to those of known maleylacetate reductases. The following gene, dxnF, encodes a 33-kDa intradiol dioxygenase which efficiently cleaves hydroxyquinol, yielding maleylacetate, the ketoform of 3-hydroxy-cis,cis-muconate. The heteromeric protein encoded by dxnGH is a 3-oxoadipate succinyl coenzyme A (succinyl-CoA) transferase, whereas dxnI specifies a protein exhibiting marked homology to acetyl-CoA acetyltransferases (thiolases). The last ORF of the sequenced fragment codes for a putative transposase. DxnD, DxnF, DxnE, DxnGH, and DxnI (the activities of most of them have also been detected in strain RW1) thus form a complete 4-hydroxysalicylate/hydroxyquinol degradative pathway. A route for the mineralization of the growth substrates 3-hydroxydibenzofuran and 2-hydroxydibenzo-p-dioxin in Sphingomonas sp. strain RW1 thus suggests itself.
Figures

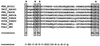
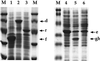
Similar articles
-
A second [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin from Sphingomonas sp. Strain RW1 can function as an electron donor for the dioxin dioxygenase.J Bacteriol. 2000 Apr;182(8):2238-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2238-2244.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10735867 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of dioxin dioxygenase of Sphingomonas sp. Strain RW1: catabolic genes dispersed on the genome.J Bacteriol. 1998 Aug;180(15):3954-66. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3954-3966.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9683494 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of Fdx1, a putidaredoxin-type [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin able to transfer electrons to the dioxin dioxygenase of Sphingomonas sp. RW1.Eur J Biochem. 1997 Aug 1;247(3):833-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00833.x. Eur J Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9288905
-
A gene cluster encoding steps in conversion of naphthalene to gentisate in Pseudomonas sp. strain U2.J Bacteriol. 1998 May;180(9):2522-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.9.2522-2530.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9573207 Free PMC article.
-
Separate Upper Pathway Ring Cleavage Dioxygenases Are Required for Growth of Sphingomonas wittichii Strain RW1 on Dibenzofuran and Dibenzo-p-Dioxin.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 May 11;87(11):e02464-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02464-20. Print 2021 May 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33741618 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A second [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin from Sphingomonas sp. Strain RW1 can function as an electron donor for the dioxin dioxygenase.J Bacteriol. 2000 Apr;182(8):2238-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2238-2244.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10735867 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 4-chlorophenol degradation gene cluster and degradation route via hydroxyquinol in Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Nov;71(11):6538-44. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.6538-6544.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16269679 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Resorcylate catabolic-pathway genes in the soil actinomycete Rhodococcus jostii RHA1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Nov;81(21):7656-65. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02422-15. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26319878 Free PMC article.
-
Four Aromatic Intradiol Ring Cleavage Dioxygenases from Aspergillus niger.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Nov 14;85(23):e01786-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01786-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31540981 Free PMC article.
-
Origins of the 2,4-dinitrotoluene pathway.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(15):4219-32. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.15.4219-4232.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12107140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armengaud J, Gaillard J, Forest E, Jouanneau Y. Characterization of a 2[4Fe-4S] ferredoxin obtained by chemical insertion of the Fe-S clusters into the apoferredoxin II from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Eur J Biochem. 1995;231:396–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

