NH2-Terminal targeting motifs direct dual specificity A-kinase-anchoring protein 1 (D-AKAP1) to either mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 10352013
- PMCID: PMC2133123
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.5.951
NH2-Terminal targeting motifs direct dual specificity A-kinase-anchoring protein 1 (D-AKAP1) to either mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
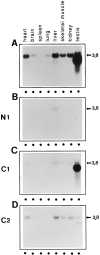
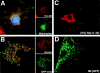
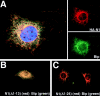
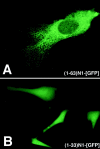
Subcellular localization directed by specific targeting motifs is an emerging theme for regulating signal transduction pathways. For cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), this is achieved primarily by its association with A-kinase-anchoring proteins (AKAPs). Dual specificity AKAP1, (D-AKAP1) binds to both type I and type II regulatory subunits and has two NH2-terminal (N0 and N1) and two COOH-terminal (C1 and C2) splice variants (. J. Biol. Chem. 272:8057). Here we report that the splice variants of D-AKAP1 are expressed in a tissue-specific manner with the NH2-terminal motifs serving as switches to localize D-AKAP1 at different sites. Northern blots showed that the N1 splice is expressed primarily in liver, while the C1 splice is predominant in testis. The C2 splice shows a general expression pattern. Microinjecting expression constructs of D-AKAP1(N0) epitope-tagged at either the NH2 or the COOH terminus showed their localization to the mitochondria based on immunocytochemistry. Deletion of N0(1-30) abolished mitochondrial targeting while N0(1-30)-GFP localized to mitochondria. Residues 1-30 of N0 are therefore necessary and sufficient for mitochondria targeting. Addition of the 33 residues of N1 targets D-AKAP1 to the ER and residues 1-63 fused to GFP are necessary and sufficient for ER targeting. Residues 14-33 of N1 are especially important for targeting to ER; however, residues 1-33 alone fused to GFP gave a diffuse distribution. N1(14-33) thus serves two functions: (a) it suppresses the mitochondrial-targeting motif located within residues 1-30 of N0 and (b) it exposes an ER-targeting motif that is at least partially contained within the N0(1-30) motif. This represents the first example of a differentially targeted AKAP and adds an additional level of complexity to the PKA signaling network.
Figures





References
-
- Andres DA, Dickerson IM, Dixon JE. Variants of the carboxyl-terminal KDEL sequence direct intracellular retention. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:5952–5955. - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Lin RY, Rubin CS. Organelle-specific targeting of protein kinase AII (PKAII) J Biol Chem. 1997;272:15247–15257. - PubMed
-
- Coghlan V, Perrino BA, Howard M, Langeberg LK, Hicks JB, Gallatin WH, Scott JD. Association of protein kinase A and protein phosphatase 2B with a common anchoring protein. Science. 1995;267:108–111. - PubMed
-
- Feliciello A, Rubin CS, Avvedimento EV, Gottesman ME. Expression of a kinase anchor protein 121 is regulated by hormones in thyroid and testicular germ cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23361–23366. - PubMed
-
- Haas IG. BiP (GRP78), an essential hsp70 resident protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Experientia. 1994;50:1012–1020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

