Yeast Bim1p promotes the G1-specific dynamics of microtubules
- PMID: 10352017
- PMCID: PMC2133138
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.5.993
Yeast Bim1p promotes the G1-specific dynamics of microtubules
Abstract
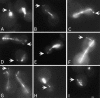
Microtubule dynamics vary during the cell cycle, and microtubules appear to be more dynamic in vivo than in vitro. Proteins that promote dynamic instability are therefore central to microtubule behavior in living cells. Here, we report that a yeast protein of the highly conserved EB1 family, Bim1p, promotes cytoplasmic microtubule dynamics specifically during G1. During G1, microtubules in cells lacking BIM1 showed reduced dynamicity due to a slower shrinkage rate, fewer rescues and catastrophes, and more time spent in an attenuated/paused state. Human EB1 was identified as an interacting partner for the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor protein. Like human EB1, Bim1p localizes to dots at the distal ends of cytoplasmic microtubules. This localization, together with data from electron microscopy and a synthetic interaction with the gene encoding the kinesin Kar3p, suggests that Bim1p acts at the microtubule plus end. Our in vivo data provide evidence of a cell cycle-specific microtubule-binding protein that promotes microtubule dynamicity.
Figures
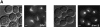
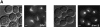
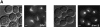





Similar articles
-
Bim1p/Yeb1p mediates the Kar9p-dependent cortical attachment of cytoplasmic microtubules.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Sep;11(9):2949-59. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.9.2949. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10982392 Free PMC article.
-
Positioning of the mitotic spindle by a cortical-microtubule capture mechanism.Science. 2000 Mar 24;287(5461):2260-2. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5461.2260. Science. 2000. PMID: 10731147
-
The regulation of microtubule dynamics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by three interacting plus-end tracking proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Jun;17(6):2789-98. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-09-0892. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16571681 Free PMC article.
-
The spindle pole body of yeast.Chromosoma. 1994 Oct;103(6):369-80. doi: 10.1007/BF00362281. Chromosoma. 1994. PMID: 7859557 Review.
-
Microtubules don and doff their caps: dynamic attachments at plus and minus ends.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Feb;13(1):92-6. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00179-4. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11163139 Review.
Cited by
-
Control of microtubule dynamics by Stu2p is essential for spindle orientation and metaphase chromosome alignment in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Sep;12(9):2870-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.9.2870. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11553724 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Dma1 and Dma2, the budding yeast homologues of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Dma1 and human Chfr.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Aug;15(8):3796-810. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-02-0094. Epub 2004 May 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15146058 Free PMC article.
-
EB1 targets to kinetochores with attached, polymerizing microtubules.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Dec;13(12):4308-16. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-04-0236. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12475954 Free PMC article.
-
Reorientation of mispositioned spindles in short astral microtubule mutant spc72Delta is dependent on spindle pole body outer plaque and Kar3 motor protein.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Apr;13(4):1366-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-07-0338. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11950945 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple mechanisms determine ER network morphology during the cell cycle in Xenopus egg extracts.J Cell Biol. 2013 Dec 9;203(5):801-14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201308001. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24297752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belmont LD, Mitchison TJ. Identification of a protein that interacts with tubulin dimers and increases the catastrophe rate of microtubules. Cell. 1996;84:623–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

